Welcome to the first class on Learning Anatomy (Gross Anatomy )
We would start with the bones of the lower limb.
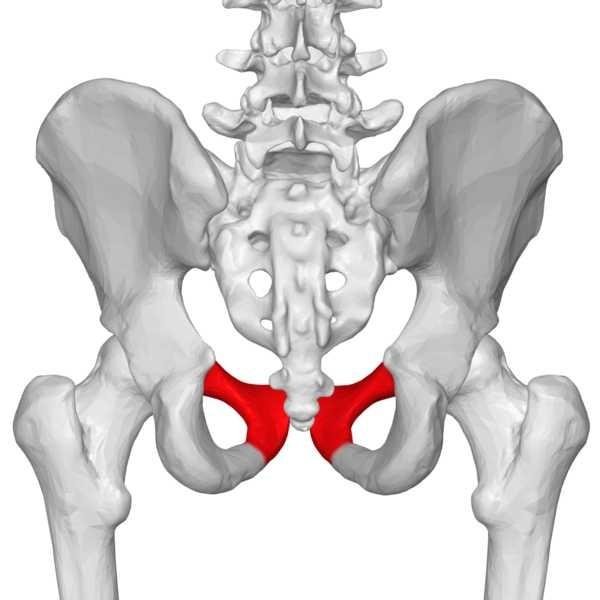
Hip Bones
The hip bone (ox coxae) is a large flat pelvic bone formed by the fusion of three important bones which vary in size and thickness. They are
- Ilium
- Ischiim
- Pubis
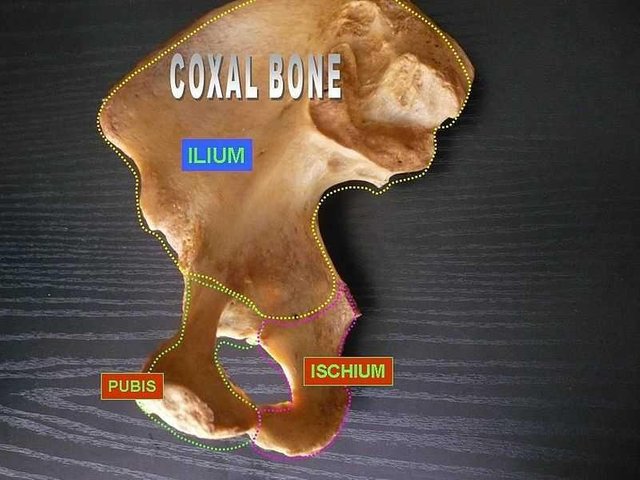
[credits ](https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Coxal_bone_(ilium,_ischium_and_pubis)
The three bones are joined together to form acetabulum, the inferior part of the ilium , the antero-inferior part of the ishium and the postero-lateral part of pubis.
Ilium
The largest part of the hip bone and contributes about 2/5 of the acetabulum. Ilium has a thick medial portion. Its a winglike structure called the alae which is a broad surface for attachment of fleshy muscles.
Its iliac crest serve as a protective number and its important site for aponeurotic attachment for thin, sheet-like muscles and deep fascia.
Ischium
The ishium is a rough bony structure in the hip bone. Its inefromedial boundary forms the Obturator foramen combined with the Pubis.
Ishium has one body and one ramus, the ramus joins with the pubis ramus to form the ischiopubic ramus which is a constituent of the Obturator Foramen.
The Ischium has a large tuberosity called the Ischial Tuberosity. You sit on on your tuberosity combined with fibrofatty tissues. Ischial spine is also present as it's a bony projection which ligaments attach to, to form Greater and lesser sciatic foramen.
Pubis
Pubis is the anterior bone of of the hip bone. It has a body and two rami. Its inferior ramus forms the ischiopubic ramus and its superior rami forms the acetabulum.
Pubis joins with the pubis of the other hip bone to form the Pubic Symphysis.
Obturator Foramen
This is a large oval, round or irregular opening in the coxae. Its boundaries are formed by the pubis and Ischium and their rami. Its usually closed by a membrane with a small gap left open for the passage of Obturator Nerve and Vessels.
Its external surface also provides attachment of fleshy muscles.
Acetabulum
This is a large cup-shaped cavity or socket on the lateral aspect of the hip bone that unites and articulates with the head of femur to form the hip joint.
All there bones of the hip combine to form the acetabulum. On its surface, there is a large depression called the Acetabular Fossa filled with fat pads.
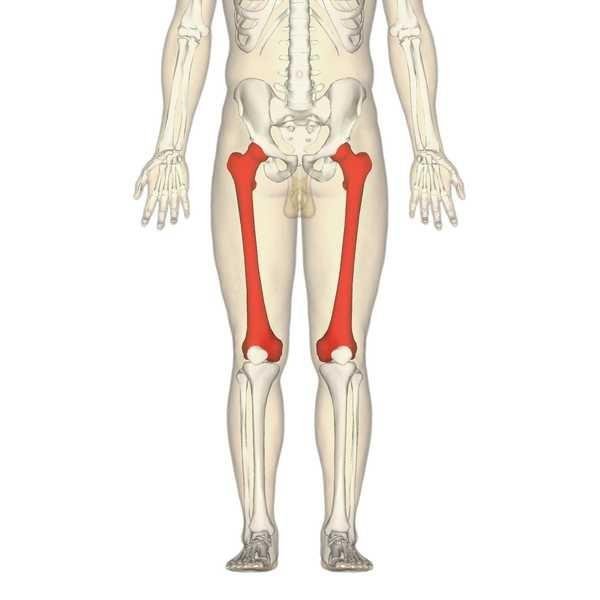
Femur
The femur is the largest, strongest and heaviest bone in the human body. It transmits weight from the hip bone to the tibia when an individual is standing. Its length is 1/4 of the human height and it consists of a head and neck (at its proximal end), shaft and condyles (at its distal end which articulates with the tibia).
Landmarks on Femur
Greater tronchanter
Lesser trochanter
Intertrochanteric line
Head
Neck
Linea Aspera
Epicondyles
Adductor Tubercles
Pectineal Line
Gluteal Tuberosity
Spiral Line
Intercondylar Fossa
Suprocondylar Lines
All these landmarks provide attachment for fleshy muscles
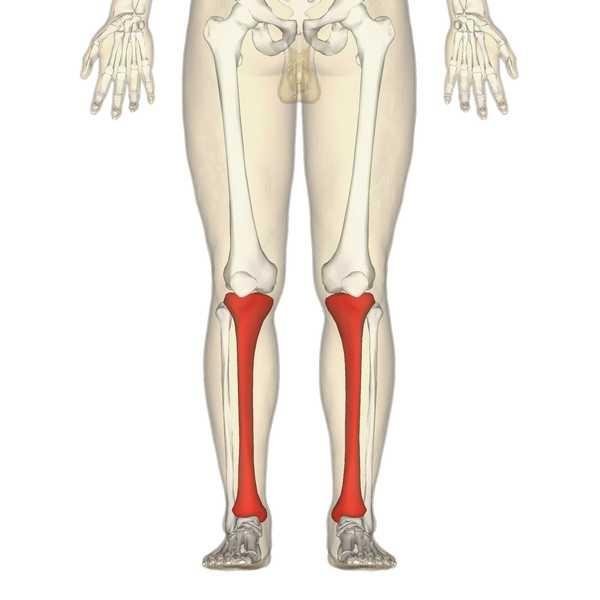
Tibia
This bony structure is located at the anterior-medial side of the leg nearly parallel to the fibula. Second largest bone in the body and transmit weight from the femur to the foot.
Tibia forms the Shin of the Leg as its Anterior border is quite prominent. It also has its own condyles for articulation with the femur.
Landmarks of Tibia
The Condyles
Soleal Line
Interosseous Membrane that runs from its lateral side
Tibial Tuberosity
Gerdys Tubercle
Fibular Notch ( where it articulates with the fibular)
Medial Malleolus (Part of the Ankle Joint)
Some of the landmarks provide attachments of fleshy muscles
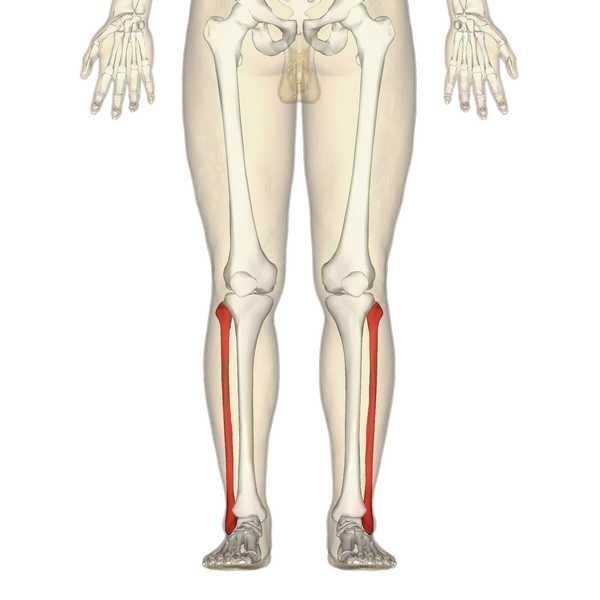
Fibular
This bone is firmly attached to the tibia and has no function in weight bearing. It only serves as muscle attachments. Eight muscles originate from it, only one attaches to it. This would be discussed as the class progresses.
Fibular shaft is twisted and marked for muscular attachment with its transverse section triangular.
Landmarks on Fibular
Lateral Malleolus (Part of the Ankle Joint)
Head
Neck
Head, Neck and Shaft all provide attachments for fleshy muscles
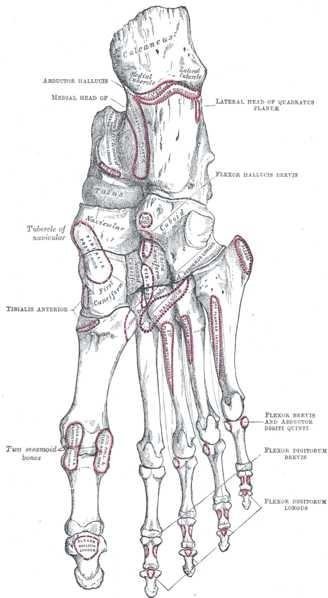
Bones of the Foot
The bones of the foot include the tarsus, metatarsus, and phalanges. We gave 7 tarsal bones, 5 metatarsals and 14 phalanges.
Tarsus
It consists of 7 bones which are the talus, calcaneus, cuboid, navicular, and the three cuneiforms making it 7 bones in total.
Talus is usually the bone in which the Tibial and fibular articulates at their distal ends. It transmit weight from the tibial to the calcaneus
Calcaneus transmits weight from the talus to the floor and to the forefoot. It also provides attachment for fleshy muscles
Navicular and Cuneiforms provide attachment for fleshy muscles and also make up the arch of the foot
Metatarsus
We have 5 metatarsus which articulates the phalanges and the tarsus bones.
The first metatarsal bone is stout and shorter than the rest while the second metatarsal is the longest.
Phalanges
We have 14 phalanges bone, the first digit having just 2 phalanges while the last 4 have 3 phalanges bones each.
The Phalanges of the first toe is called the Hallux
Clinical Correlates
Fractures of the Hip bone
Coxa Vara and Coxa Valga
Dislocation
Fractures of the Femur
Fractures of the Tibia
Fractures of the Fibular
Fractures of the Talar
Calcaneal Fracture
Metatarsals Fracture
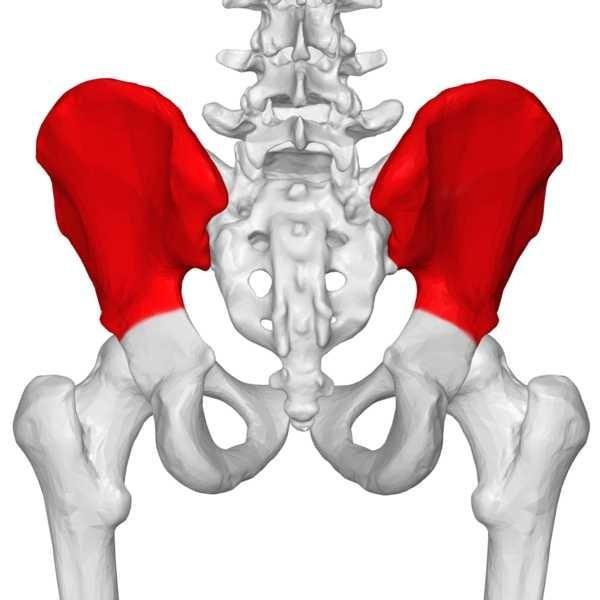
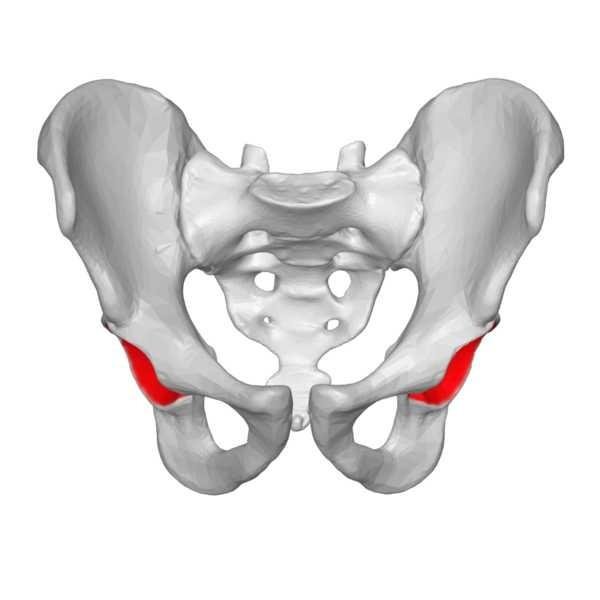
Arh this post is nostalgic, takes me back to school days. Wonderful posts and great illustrations. Excellent
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks sir
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This is amazing I just refreshed my memory on the structure of the anatomy of the lower limbs.
Proud of you
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Well
I made it simple but well summarised for every kinda of persona to understand
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Never knew all those english are for bones
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Keep following me
Then you would learn alot about your own body 😘
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
U made me remember my school days.you explained them in details welldone
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks sir
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
You are totally correct on fibula not having function in load bearing. A friend once broke his and could walk without it. Interesting to see my high school biology classes again.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Yes
Reason the fibular is usually used for bone grafting
Though serious fracture to the bone can damage nerves
Causing foot drop and inability to evert the foot and plantarflex the foot
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I remember this in secondary school biology.. It looked difficult then but reading this made it look like cheese. Well done.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Tried my possible best to make it as simple and well detailed as possible
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Sincerely this article simplifies the whole learning process. If this method is applied in schools, I'm sure a lot of students will grasp the concepts in no time.
I personally learnt about some bones i didn't know about before. Nicely written.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit