In 1964, a physicist named peter Higgs, was intrigued about the formation of Mass and other Scientists ideas about it. Specifically, the question was why some subatomic particles had bigger masses than others, while others had no mass at all. Nobody understood this at that time and Higgs added his own thoughts and proposed that there was an energy field that filled the entire universe. This energy (currently now called the Higgs field) would interact with the particles and give them their Mass.
He proposed that very massive(heavy) particles will interact a lot with the field while Massless(light) particles would not interact at all. The lightest subatomic particles would be electrons while the heaviest are the Top quarks. The Higgs boson is the smallest part of the Higgs field or basically a unit of the Higgs field. The scientific community did not believe his theory as it could not be proven then.
The Standard Model as reference
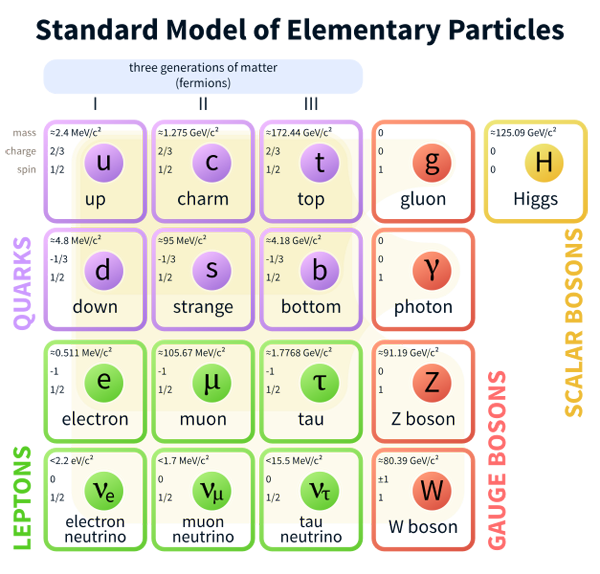
Over the years, Scientists have stuck with the Standard Model for answers about our Universe. The standard model is a theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces. The three forces are Electromagnetic, Weak, and Strong forces. The forth which was gravity, was not in the model. The Subatomic matter particles can be described either as fundamental or composite. The fundamental matter particles are quarks and leptons. Protons and neutrons are basically composites of quarks while an electron is a lepton.
Matter (quarks & leptons)
• Hadrons (composites made of quarks or antiquarks)
Baryons (made of three quarks) [composite fermions] {stable}
Mesons (made of one quark & one antiquark) [composite bosons] {unstable}
• Leptons (fundamental particles)
Phenomena not explained by the Standard model include
• Gravity
• Dark matter and dark energy
• Neutrino
• Matter–antimatter asymmetry
The CERN experiment
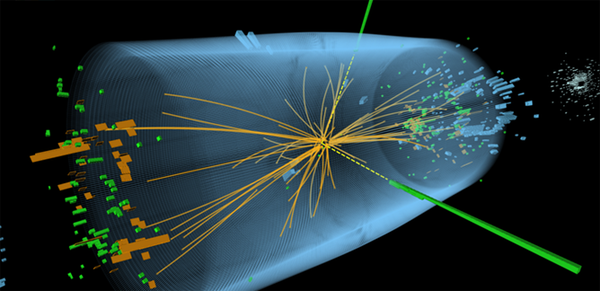
CERN or European Organization for Nuclear Research is a European research organization that controls the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. The particle accelerator or Large Hadron Collider is located underground in a 27-kilometer tunnel beneath the Swiss/French border. It was built between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and engineers from over 100 countries. On 4 July 2012, two experiments; the ATLAS and CMS were conducted at the CERN's Large Hadron Collider. The experiment was conducted to prove the existence of the Higgs boson or "God particle"
Atlas: The Atlas which is the largest volume particle detector ever constructed, used an advanced trigger system to control the detector. It then decides which events to record and which to ignore. Advanced data-acquisition and computing systems are then used to analyze the collision events and then recorded. A total of 3000 scientists from 174 institutes in 38 countries worked on the ATLAS experiment
CMS: The Compact Muon Solenoid or CMS is a general-purpose detector. It is built around a huge solenoid magnet. The solenoid generates a field of 4 tesla or 100,000 times the magnetic field of the Earth. The entire team was made up of 4300 particle physicists, engineers, technicians, students and support staff from 182 institutes in 42 countries. It was the largest international collaboration in history.
Methodology
The Hadron colliders fires particles and make them go very fast or near the speed of light and slam them into each other. When they slam into each other, the containing field i.e. the Higgs field will “jiggle” and flicker off a spark of the field known as a Higgs particle. The particle is not easy to find as just one in a trillion collisions will produce a Higgs particle. The two detectors will try to detect this phenomenon.
Result
On 4 July 2012, both experiments of Atlas and CMS announced they had each observed a new particle in the mass region around 126 GeV
Conclusion
Thanks to technology, since its discovery, the particle has been shown to behave, interact, and decay in many of the ways predicted for Higgs particles. It showed us that the theorists had been right to look towards the Standard Model for answers about our Universe. If we did not get a good result, it would have raised many questions about the theory, and our universe. Instead, it raised few questions and gave no new clues about to where to look next.
Thanks for reading.

Being A SteemStem Member
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
If I may shoot a few comments... ;)
People should stop calling the Higgs boson the god particle. This is nothing (but really nothing) to do with God.
Also note that CERN is not an experiment. It is a research center conducting many many experiments. The LHC project is just one of the numerous things happening at CERN.
Theorists already know that the standard model is NOT the answer to how the universe works... This is why searches new phenomena play an important role at the LHC.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks for the explanation. I wish I could come for the Steemit meetup at CERN. However, I have started studying your crash course.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Maybe for the next time? :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit