Understanding the device, stepper motor

Stepper motor
Image
Stepper motors are electromechanical devices that work by converting electronic pulses into discrete mechanical motions. Stepper motor moves based on the order of pulses given to the motor. Therefore, to drive it required stepper motor controller that generates periodic pulses. The use of stepper motors has several advantages compared to the use of ordinary DC motors. Advantages include:
- The rotation angle of the motor is proportional to the input pulse making it more manageable.
- The motor can directly provide full torque at the start of moving
- The position and movement of repetitions can be determined precisely
- Has a very good response to start, stop and turn (rotation)
- Very realibel due to the absence of brush in contact with the rotor as in DC motor
- Can produce slow rotation so that the load can be coupled directly to its axis
- Frequency of rotation can be determined freely and easily over a wide range.
The working principle of stepper motor
Stepper motors are control devices that convert input bits into rotor positions. The bits are derived from the input terminals that exist on the stepper motor into the magnetic poles in the motor. When one of the terminals is provided with a voltage source, the terminal will activate the poles inside the magnet as the north pole and the unstained pole as the south pole. With the presence of two poles inside this motor, the rotor inside the motor that has a permanent magnetic pole will lead according to the input poles. The north pole of the rotor will lead to the south pole of the stator while the south pole of the rotor will lead to the stator's north pole.
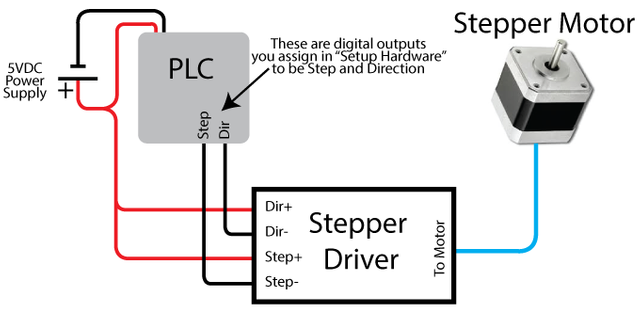
Control of stepper motor
Image
The working principle of a stepper motor is similar to a DC motor, equally stacked with a DC voltage to obtain a magnetic field. When a DC motor has a fixed magnet on the stator, the stepper motor has a fixed magnet on the rotor. The specification of the stepper motor is the number of phases, the magnitude of the degree of degree per step, the magnitude of the supply voltage volt for each winding, and the amount of current required for each winding.
The stepper motors can not move themselves continuously, but move discrete per step according to their specifications. To move from one step to the next step takes time and produces a large torque at low speed. One of the important stepper motor characteristics is the presence of retaining torque, which allows the stepper motor to retain its position which is useful for in-stepper motor applications that require a start and stop state.
Characteristics of stepper motor
Voltage
Each stepper motor has the average voltage written on each unit or listed on the datasheet of each stepper motor. This average voltage must be observed carefully because if it exceeds the average voltage it will cause heat that causes the rotation performance is not maximal or even the stepper motor will be damaged by itself
Resistance
The resistance per coil is another characteristic of the stepper motor. This resistance will determine the current that flows, but it will also affect the maximum torque and speed and stepper motors.
Degrees per step
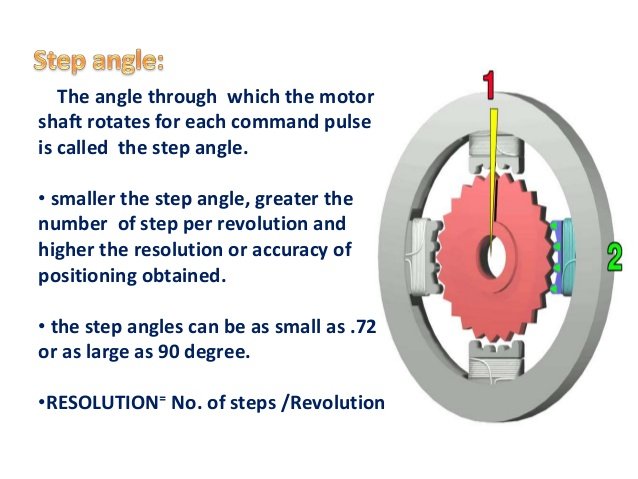
Image
The degree of rotation per step is the most important parameter in choosing a stepper motor because it will determine the smallest step of motion (resolution). Each stepper motor has its own specifications, including 0.72 ° per step, 1.8 ° per step, 3.6 ° per step, 7.5 ° per step, 15 ° per step, and even 90 ° per step. In operation we can use two principles that is full step or half step. With full step means stepper motor rotates according to specification degree per stepnya, while half step mean stepper motor rotate half degree per step from stepper motor specification.
The types of stepper motors
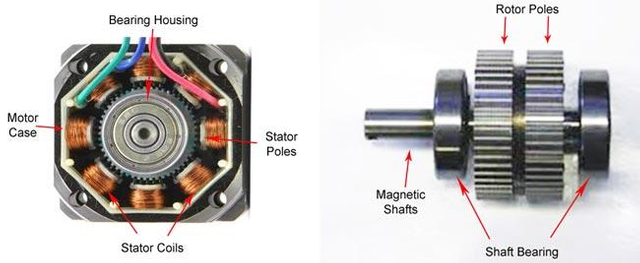
Inside a stepper motor
Image
Based on the rotor and stator structure on the stepper motor, the stepper motor can be categorized into 3 types as follows:
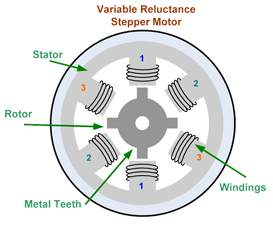
- Motor Stepper Variable Reluctance (VR)
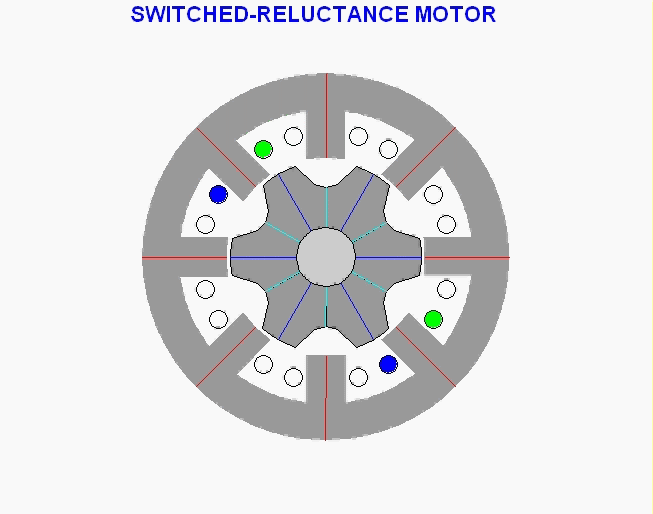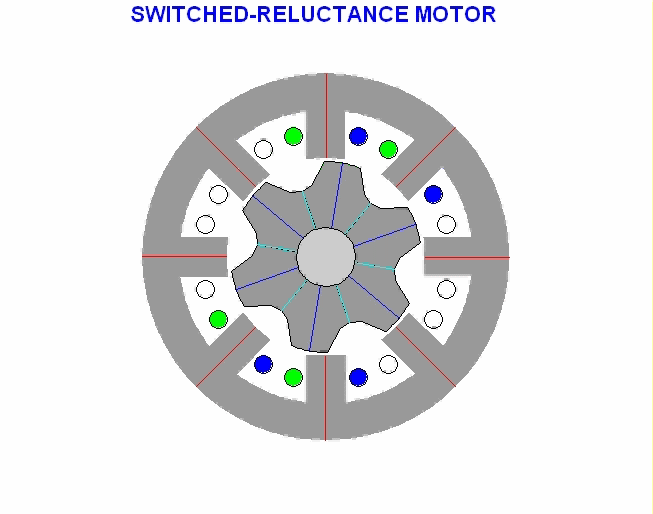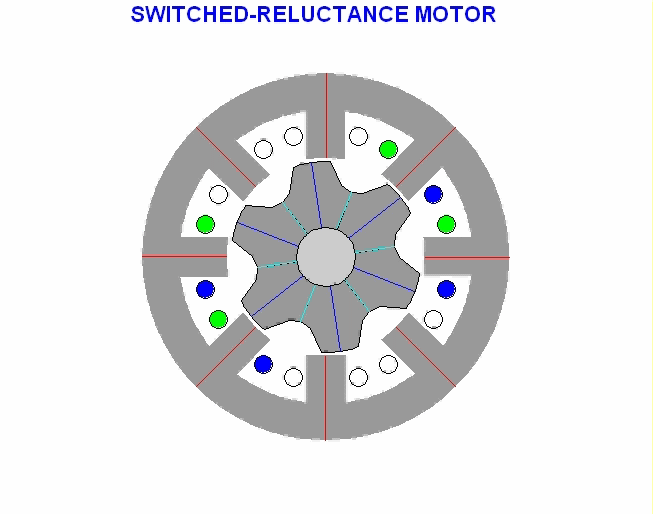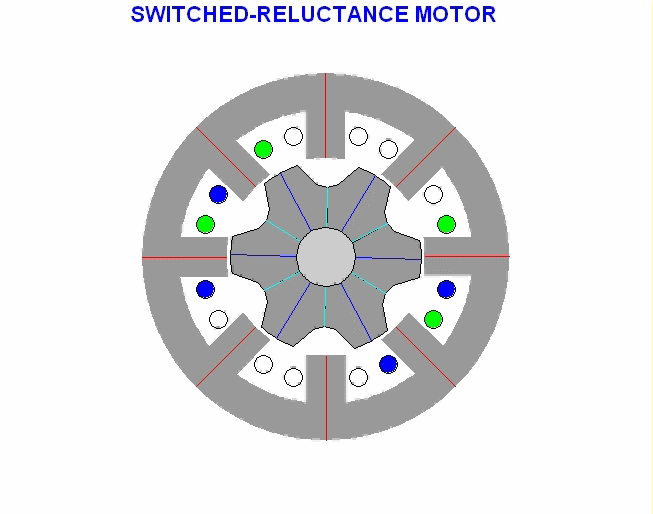
Stepper motor type variable reluctance (VR)
Image
This type of stepper motor has long existed and is the type of motor that is structurally most easily understood. This motor consists of a soft iron rotor with several serrations and a stator winding. When the stator winding is energized with DC current, the poles become magnetized. The rotation occurs when the rotor teeth are attracted by the stator poles. Here is a cross section of a variable reluctance stepper motor (VR):
Stepper motor type variable reluctance (VR)
Image
- Stepper Motor Permanent Magnet (PM)
This stepper motor has a rotor shaped like a tin consisting of a permanent magnet layer alternated with opposite poles.
the magnetic flux intensity in this motor will increase so as to produce greater torque. This type of motor usually has a low step resolution that is between 7.50 to 150 per step or 48 to 24 steps per lap. Here is a simple illustration of the permanent magnetic stepper motor type:
Permanent magnetic stepper motor (PM)
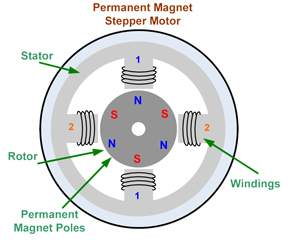
stepper motor permanent magnet (PM) type
Image
- Stepper Motor Hybrid (HB)
Hybrid stepper motor has a structure that is a combination of both types of stepper motors before. The hybrid type stepper motor has teeth as in the VR type motor and also has a permanent magnet arranged axially on the shaft of the axle like the PM type motor. Motor type is most popular in various applications because of better performance. Hybrid motors can produce high step resolutions ranging from 3.60 to 0.90 per step or 100-400 steps per turn. Here is a cross section of a hybrid type stepper motor:
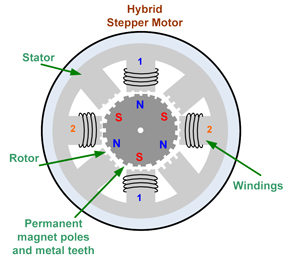
stepper motor hybrid type
Image
Based on the design method of rangkain controller, stepper motor can be divided into 2 types of unipolar stepper motor and bipolar stepper motor.
- Unipolar Stepper Motor
Unipolar stepper motor control circuit is easier to be designed because it requires only one switch / transistor each winding. To run and stop this motor simply by applying a digital pulse consisting only of positive and zero voltage (ground) on one of the motor's wound terminals while the other terminals are fed with the constant positive voltage (VM) of the center tap of coil as in the following picture.
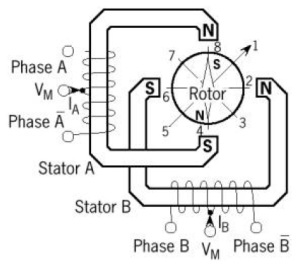
Stepper motor with unipolar winding
- Stepper motor Bipolar
For stepper motors with bipolar coils, pulse signals are required to vary from positive to negative and vice versa. So at each winding terminal (A & B) must be connected to a signal that swings from positive to negative and vice versa. Therefore a control circuit is somewhat more complex than the control circuit for unipolar motors. Bipolar stepper motors have advantages compared to unipolar stepper motors in case of greater torque for the same size.
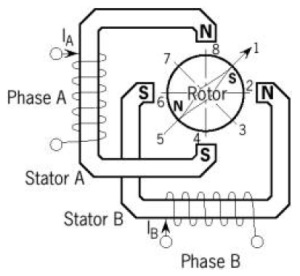
Stepper motor with bipolar winding
Differentiating the two, unlike the unipolar stepper motor, the bipolar stepper motor has two leads per phase. But neither of which are common. Static friction effects do happen with a H-bridge with certain drive topologies. however usually this can be reduced with dithering the stepper motor signal at a higher frequency.
Bipolar stepper motors are a bit more difficult to operate, while the unipolar motor does feature twice the amount of wire in the same space. Different projects will require different types and settings of stepper motors.
References used:
- http://www.robotpark.com/Stepper-Motors
- http://velocio.net/plc-stepper-motor-control/
- https://www.engineersgarage.com/articles/stepper-motors
- http://blog.inventables.com/p/stepper-motors.html
- http://www.ni.com/white-paper/14891/en/
- https://www.circuitspecialists.com/blog/unipolar-stepper-motor-vs-bipolar-stepper-motors/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stepper_motor
Support @steemstem and the #steemstem
project - curating and supporting quality STEM
related content on Steemit

This post has received a 1.06% upvote from thanks to: @chotho.
thanks to: @chotho.
For more information, click here!!!!
Send minimum 0.050 SBD/STEEM to bid for votes.
Do you know, you can also earn daily passive income simply by delegating your Steem Power to @minnowhelper by clicking following links: 10SP, 100SP, 500SP, 1000SP or Another amount
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit