An earthquake is the sudden movement of the Earth (with capital letters, since we refer to the planet), caused by the sudden release of accumulated energy for a long time. The Earth's crust is made up of a dozen plates approximately 70 km thick, each with different physical and chemical characteristics. These plates ("tectonics") are being accommodated in a process that takes millions of years and have been giving the shape we know today to the surface of our planet, originating continents and geographical reliefs in a process that is far from being completed. Usually these movements are slow and imperceptible, but in some cases these plates collide with each other like gigantic ice floes on an ocean of magma present in the depths of the Earth, preventing their displacement. Then one plate begins to move over or under the other causing slow changes in the topography. But if the displacement is difficult, a tension energy begins to accumulate that at some moment will be released and one of the plates will move abruptly against the other, breaking it and then releasing a variable quantity of energy that originates the
The underground activity originated by a volcano in the process of eruption can originate a similar phenomenon.
In general the term earthquake is associated with seismic movements of considerable dimension, although rigorously its etymology means "movement of the Earth".
The earth's crust is composed of different tectonic plates, each of a certain composition and thickness. The process of evolution of the planet runs its course and these plates move constantly, seeking accommodation. The movements of the plates are imperceptible and very slow but when two plates try to fit into the same space, they collide and their natural movement leads them to move one below the other.
The zones where two plates collide and move receive the name of "faults" and accumulate energy coming from this tectonic tension, being these points the places with more probabilities of originating earthquakes. The point of the confluence of plates where the earthquake originates denominates "hipocentro." The projection of said point on the terrestrial surface is denominated "epicenter".
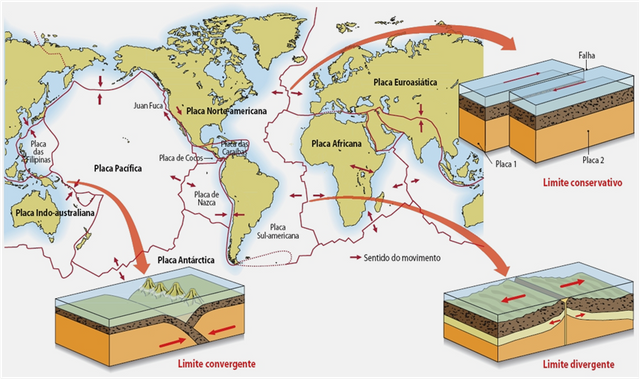
Limits of plates
It's where the plates converge and interact. There are three classes:
Divergent or constructive: the plates separate and move away from each other, for example, the mid-Atlantic ridge, formed by the separation of the plates of Eurasia and North America and those of Africa and South America, or the Great Rift Valley.
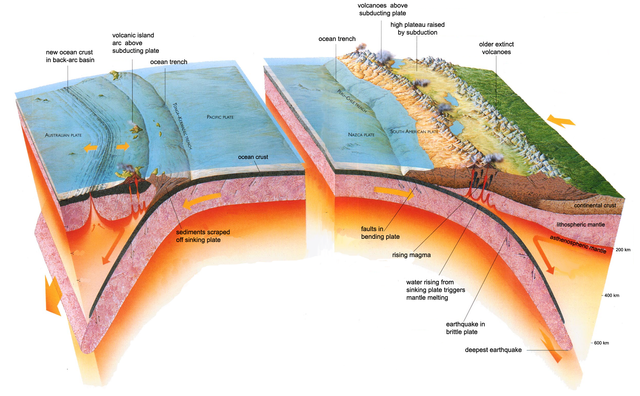
Convergent or destructive: one plate collides with another, the result of that collision depends on the type of lithosphere of the plates. If an oceanic plate collides with a continental one, the oceanic plate is pushed underneath forming a zone of subduction. On the surface there will be an oceanic pit in the water and a group of mountains on land. If two continental plates collide, extensive mountain ranges are created, such as the Himalayas, the result of the collision between the Indo-Australian plate and the Eurasian plate. If there are two oceanic plates that collide, an arch of islands is formed, like Japan.
Transformant or conservative: the edges of the plates slide along a transformation fault. The plates do not slide continuously but, due to friction, both plates accumulate tension until that accumulated energy is released in the form of movement of the fault, causing earthquakes. An example of a conservative limit would be the San Andreas fault, in western North America.
Seismic regions
There are regions of the Earth in which the incidence of earthquakes is higher than in others and the seismographs (instruments to measure earthquakes) and prediction centers do not even have a rest day. The repeated succession of earthquakes in some parts of the world has allowed geologists to determine the regions of greatest seismic activity. If you live in one of these areas where earthquakes are common you should think about what to do in case of an earthquake.
HISTORY
The study of earthquakes is called Seismology and is a relatively recent science. Until the eighteenth century objective records of earthquakes are scarce and there was no real understanding of the phenomenon. From the explanations related to divine punishments or Earth responses to human misbehavior, it went on to pseudo-scientific explanations as they were originated by the release of air from caverns present in the depths of the planet.
The first earthquake that has reference occurred in China in the year 1177 BC There is a Chinese Catalog of Earthquakes that mentions a few dozen more such phenomena in the following centuries.
In the History of Europe the first earthquake appears mentioned in the year 580 A of C, but the first one clearly described dates from the middle of the XVI century.
The oldest known earthquakes in America occurred in Mexico, at the end of the 14th century and in Peru in 1741, although there is no clear description of its effects.
Since the seventeenth century many stories about earthquakes have begun to appear, but it seems that most of them were distorted or exaggerated.
In North America an important series of earthquakes occurred between 1811 and 1812 near New Madrid, Missouri, standing out one of estimated magnitude around 8 degrees. The morning of December 16, 1811. On January 23 and February 7, 1812 there were two other significant earthquakes in the area, especially the last mentioned, whose replicas lasted months and was felt in areas as far away as Denver and Boston. Because they were not so populated then, the cities did not register too many deaths or damages.
The same thing did not happen in 1906 when more than 700 victims died in San Francisco and the city was devastated by the earthquake and the subsequent fire in the largest earthquake in the history of the United States. 250,000 people were left homeless.
In Alaska, on March 27, 1964, an earthquake of even greater energy was registered, but because it is an area of low population density, the damage to the population was not as severe, with only 107 people dead, which is not so much it is considered that the earthquake was felt in an area of 500,000 square miles and ripped the trees off the ground in some areas
MEASUREMENT OF EARTHQUAKES
It is done through an instrument called seismograph, which records on a paper the vibration of the Earth produced by the earthquake (seismogram). Inform us about the magnitude and duration.
This instrument records two types of waves: the surface waves, which travel through the Earth's surface and produce the highest vibration of this (and probably the greatest damage) and the central or corporal vibrations that travel through the Earth from its depth .
Faults
is the contact surface between two blocks separated by a break in the earth's crust that move differentially with respect to each other. They can extend spatially for several hundred kilometers and temporarily for several million years. An active fault is one in which displacement has occurred in the last 2 million years or in which seismic activity is observed. There are several famous faults in the world, one of them is the San Andreas Fault.
Normal failure: They are inclined fractures with blocks that slide vertically mainly. In this case the blocks are called Roof and Floor, the roof being the block that lies on the inclined fracture. If the roof of the fault moves down, the fault is of the normal type. Otherwise it is a reverse fault
Strike-slip fault: Vertical failures in which only horizontal displacement occurs.
Magnitude of Richter Scale
It represents the seismic energy released in each earthquake and is based on the seismograph record. It is a scale that grows in potential or semi logarithmic form, so that each point of increase can mean an increase in energy ten or more times greater. A magnitude of 4 is not double of 2, but 100 times greater.
Magnitude on the Richter scale Effects of the earthquake
Less than 3.5 Usually does not feel, but is registered
3.5 - 5.4 It is often felt, but only causes minor damage.
5.5 - 6.0 Causes light damage to buildings.
6.1 - 6.9 May cause severe damage in heavily populated areas.
7.0 - 7.9 Major earthquake. It causes serious damage.
8 or greater Great earthquake. Total destruction to nearby communities.
These are the 10 largest earthquakes that have been produced in the country as a result of history
- Valdivia, Chile (1960)
- Alaska (1964)
- Sumatra (2004)
- Japan (2011)
- Kamchatka (1952)
- Maule Region, Chile (2010)
- Ecuador (1906)
- Rat Islands, Alaska (1965)
- Indonesia (2005)
- Tibet (1950)
I HOPE YOU LIKE THE CONTENT THANK YOU
References for information
https://www.facebook.com/Earthquakes-116342575615324/
https://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html
https://quizlet.com/28295556/chapter-8-earth-science-flash-cards/

Being A SteemStem Member
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
You received a 10.0% upvote since you are not yet a member of geopolis.
To read more about us and what we do, click here.
https://steemit.com/geopolis/@geopolis/geopolis-the-community-for-global-sciences-update-3
If you do not want us to upvote and comment on your posts concerning earth and earth sciences, please reply stop to this comment and we will no longer bother you with our love ❤️
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I liked the post that you talked about the plates of the planet earth
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit