The marriage between medicine and nanotechnology is becoming a nightmare for cancer. The combat of the disease on a molecular scale allows early detection of the disease, identifying and attacking more specifically the cancer cells. That is why the National Cancer Institute of the United States (NCI) has launched the "Alliance for nanotechnology in cancer", a plan that includes the development and creation of miniature instruments for early detection.
Source
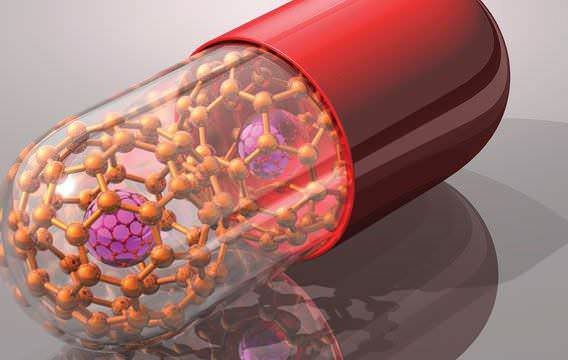
In the administration of medicines, the new techniques are already a fact. "The drug release nanosystems act as transporters of drugs through the body, providing them with greater stability against degradation, and facilitating its diffusion through biological barriers and, therefore, access to target cells" , explains María José Alonso, a researcher at the University of Santiago de Compostela, who has been working on this line since 1987. In the treatment of cancer, she says, "these nanosystems facilitate access to tumor cells and reduce the accumulation of the drug in cells healthy and, therefore, reduce the toxic effects of antitumor drugs ".
From the United States have developed another alternative based on artificial molecules known as dendrimers. These are three-dimensional branched structures that can be designed on a nanoscale with extraordinary precision. The dendrimers have several free ends, in which molecules of different nature can be coupled and transported, from therapeutic agents to fluorescent molecules. For the study, a powerful medicine against cancer, methotrexate, was applied to some branches of the dendrimer. In others, it incorporated fluorescent agents, as well as folic acid or folate, a vitamin necessary for cellular functioning. The folate molecules in the nanoparticle cling to the cell membrane receptors and they think they are receiving the vitamin. By allowing folate to penetrate the membrane, the cell also receives the drug that poisons it.

Source
Infectious diseases are another of the great objectives of current medicine. They have also developed nanoparticles that allow administering, in the form of simple nasal drops, some vaccines that until now had to be injected. Its efficacy has been demonstrated, so far, for anti-tetanus and anti-diphtheria vaccines.
No less important is the battle that is being waged around the world against diabetes, and in which nanotechnology has a lot to say. The developed nanoparticles are being used in experiments in the clinic to study their use as vehicles to administer insulin orally, nasally or pulmonary. They have created a device that can be injected into the bloodstream and act as an artificial pancreas, releasing insulin. The technique developed consists of encapsulating cells that produce insulin in containers with walls with nanopores, which due to their size can only be crossed by molecules such as oxygen, glucose or insulin. In this way, the walls of the capsule prevent these insulin-producing cells from being recognized as foreign by the antibodies, while the pores allow the release of insulin and the entry of nutrients, such as sugars and nutrients. The innovative technique has a potential for the cure of other diseases such as Parkinson's disease, through the release of dopamine in the brain, or Alzheimer's.
If the therapies are experiencing drastic changes, the diagnosis is not far behind. Hand in hand with nanotechnology we enter the era of molecular diagnosis, sophisticated and precise, which makes it possible to identify genetic diseases, infectious or even small alterations of proteins at an early stage.
Not in vain, this discipline has contributed to the creation of biochips, which allow obtaining large amounts of information working on a very small scale. With nanoscale biochips it is possible to obtain in a short time a lot of genetic information - both from the individual and from the pathogen - that will make vaccines, measure resistance of tuberculosis strains to antibiotics or identify the mutations that some genes undergo. They play a prominent role in certain tumor diseases, such as the p53 gene in colon and breast cancers.
The development of sensors on a molecular scale seems to have no limits. Recently, a team of scientists from Harvard University discovered that ultra-fine silicon wires can be used to detect the presence of individual viruses, in real time and with great precision. In the clinical environment, the extreme sensitivity of the arrays of nanowires could detect viral infections in their early stages, when the immune system is still unable to act.
Source
Nano-robots
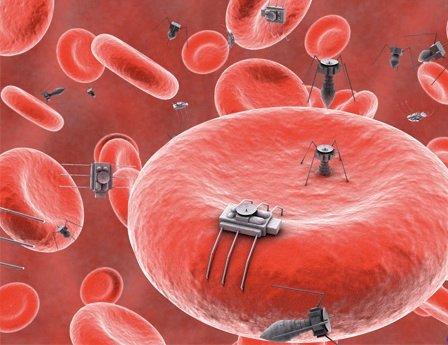
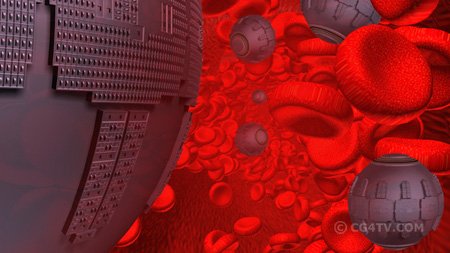
The molecular repair machines that will travel through the bloodstream, with the capacity to act on DNA (genetic diseases), modify proteins or even destroy whole cells, in the case of tumors, remain for the time being. However, some experts have already dared to anticipate how those future nano-robots will be.
Source
This is the case of Robert Freitas, a researcher at the Molecular Manufacturing Institute of California, who has created a kind of artificial red blood cell called respirocyte. With a single micron in diameter, this spherical robot imitates the action of natural hemoglobin found inside the red blood cells, although with the ability to release up to 236 times more oxygen per unit volume than a natural red blood cell. The respirocytes will incorporate chemical sensors, as well as pressure sensors. In this way they will be prepared to receive acoustic signals from the doctor, who will use an ultrasound transmitting device to give them orders in order to modify their behavior while they are inside the patient's body.

Source
Freitas has also designed microbivores, mechanical phagocytes designed to destroy any microbe in our bloodstream. Using a digestive protocol and discharges will act, according to estimates its creator, up to 1000 times faster than natural defenses.
Source
For more information visit the following links
- http://www.magzter.com/article/Health/Scientific-India/Nanomedicine-The-Medicine-For-Future-Generation
- https://app.curiositystream.com/video/151/how-will-nanotechnology-revolutionize-medicine
- http://healthieragain.com/2017/01/medicine-and-nanotechnology/
- http://www.rfreitas.com/