Steering a vehicle by manual effort became very difficult especially as vehicles became heavier and off-course humans began to complain. This emphasized the need for a steering assist. This has been accomplished by adding a hydraulic system to the steering mechanism.
Come to think of it! Have you even wondered why the steering wheels of your car feel so soft? or Have you ever experienced hardening of your steering wheels when your steering fluid is short?
You may probably want to read this!
Here, we will be looking at the recirculating-ball steering mechanism and its improvement with the inclusion of the hydraulic system.
First lets take a quick look at the recirculating-ball steering mechanism in general
This steering mechanism uses a cam and lever mechanism consisting of the following components.
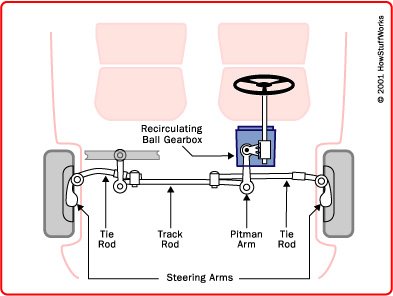
Components:
- A steering shaft and cam (recirculating-ball gearbox)
- A pitman arm lever
- A pitman arm shaft and pitman arm
- A drag link (track rod)
- A tie rod.
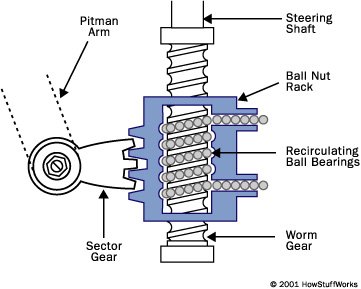
The steering wheel is connected to a threaded rod, similar to a bolt, which sticks into the hole in the block. When the steering wheel is turned by a driver, it turns the bolt and instead of twisting further into the block the way a regular bolt would do, it is held fixed so that when it spins, it moves the block, which in turn move the gear that turns the wheels. This is a little convenient to achieve by a driver while in motion but as the speed of the car reduces, it becomes much more difficult.
During off-road driving, the steering may become impossible to turn because the turning force (torque) the driver has to generate becomes increasingly high. This brought about the development of an assisting mechanism known as the power steering! The hydraulic power steering assist mechanism is going to be discussed here.
To obtain the assist, a hydraulic system is added to the cam and lever mechanism. The hydraulic steering mechanism is made up of five basic components!
- A reservoir
- Pump
- Relief valve
- Control valve
- Power cylinder
These components operate on the principle of pressure differential.
Pressure differential is simply difference in applied pressure between two points. Where force applied results in pressure generation at a point and the pressure is then multiplied by a device on the other end.
Differential pressure steering is a means of steering an automobile by applying more or less drive torque to one side of the vehicle wheels than the other.
How does the hydraulic steering mechanism assist?
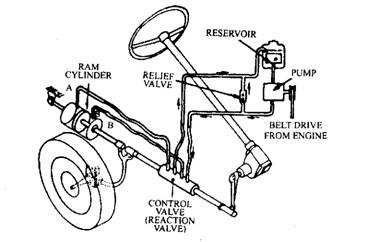
The reservoir in the hydraulic system supplies steering fluid (hydraulic). The pump driven by the engine through belt drives delivers the fluid under pressure to the relief and control valves. The control valve actuated by the steering shafts directs the fluid through to the power cylinder.
The power cylinder converts the hydraulic pressure into mechanical force by means of a piston based on the pressure differential principle.
In other for the hydraulic steering assist to operate, it is not only necessary for the cam to rotate but it must be able to move up and down. A splin connection makes it possible.
The pitman arm lever which actuates the pitman arm has one end fastened to the piston rod and the other to the steering cam.
When the steering shaft is turned, it requires a greater effort to turn the pitman arm shaft and lever and to compress the springs at either ends of the cam. This is so because the pitman arm shaft and lever are connected to the front wheels. This action causes the cam to move up or down depending on the direction that the steering wheel is turned.
This up and down movement of the steering cam actuates the control valve through the valve lever linkage. The control valve is the heart of the hydraulic steering system. The control valve has a spur that directs and controls the flow of fluid through the power cylinder. Full pressure of the hydraulic system is applied with only a few movement of an inch of control valve travel.
As the steering wheel is turned, the up and down movement of the cam actuates the control valve lever shifting the position of the valve spool. The spool ends directs the flow of fluid from the pump to the power cylinder. This flow of fluid causes an immediate pressure increase on one side of the piston in the power cylinder.
At the same time, fluid from the other side of the piston is displaced by a pressure differential and forced up and around the unrestricted passage way in the control valve to the outlet leading back to the reservoir.
The pressure differential in the power cylinder moves the piston and piston rods thus supplying a mechanical force to the pitman arm lever turning the wheels in the desired direction.
On continual turning, it comes to a point when the piston end its travel in the power cylinder, the pump still continues to deliver fluid causing and increase in operating pressure. The relief valve provides an escape for this excess pressure back to the reservoir.
After completing a turn, the driver releases tension on the steering wheel and the steering system is returned to its original position (straight ahead position) allowing the hydraulic system to return back to its neutral position.
To steer in the opposite direction, the cam actuates the control valve lever the other way and pressure is now directed to the opposite side of the power cylinder piston.
Additional information
The electric power assisted steering (EPAS) is the new technology now adopted. This is a rather simpler, more efficient and more compact design.
There is also an electrically powered hydraulic steering in which the belt driven pump is replaced by an electric pump. This is still a more efficient power steering mechanism as the pressure generated by the hydraulic pump while not steering is a waste.
The steering assistance arrangement have to satisfy certain requirements.
- It must be ‘fail-safe’, meaning: if the hydraulic system fails, the driver has to still be able to retain effective control of the vehicle.
- The amount of steering assistance should be equivalent to the effort put by the driver and the driver must be able to retain the ‘feel’ of the wheels. i.e It shouldn't be too easy for the driver to steer. The wheels may start steering the steering wheels.. Easy is enough.
References
power assisted steering in automobile
Historically speaking about cars
All images are copyright free
perfect ,,, i like with successful people like you. !! thanks.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Is the mechanical engineering field going electrical or should I say mechatronics.. .. With electric power assisted steering there will be need for recharge... Is there any plan for that?
Good discovery sir
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Good observation! The fact is that the electric motor in the EPS uses a sensor technology which receives signals of vehicle speed, steering angle, steering torque etc. This sensor helps the motor rotate delivering the required torque at the required time.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
That's Good
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit