Today we're exploring a major breakthrough that might give us the keys to reversing much pain and many diseases.
(If science is not for you, just skip the Science section.)
We all have loved ones that at one time or another had to suffer from pain and disease. Science is getting close to taking control of it.
Too much inflammation causes much suffering
One thing that is common among almost every disease, cancer and chronic pain is inflammation. Our bodies naturally make inflammation to resist damage by bacteria and to help us heal. But too much inflammation is not good. Most diseases and cancers have taken advantage of this and cause our bodies to produce too much inflammation. In fact, it appears that without this over-production of inflammation most cancers and diseases could not survive.
The Science
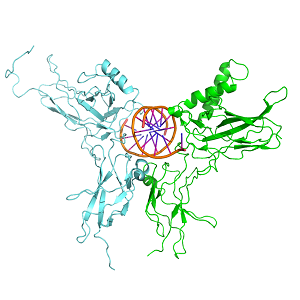 DNA (orange), NF-κB (green), RelB (cyan)
DNA (orange), NF-κB (green), RelB (cyan)
This computer generated image shows the root cause of inflammation. NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) protein (green) with RelB (cyan) interacts with DNA (orange) causing DNA to produce the molecules that make inflammation.
NF-κB is found to be overly active in many inflammatory diseases, such as arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis, chronic back pain and many others.
The scientist
Dr. Ranjan Sen, Ph.D discovered NF-κB, the key to inflammation. 
Human trials
Researchers are now at the stage of human trials to test new drugs that are designed to reduce the amount of activated NF-κB that our cells make. This is expected to reduce the high levels of inflammation and allow our bodies to heal faster.
Food
Besides the new miracle drugs coming available soon, we can reduce inflammation with certain foods and spices. Some of the better ones are turmeric, ginger, garlic and hot peppers.

Turmeric is the main ingredient in curry. It's also found in mustard and several other foods.
As you can see below, turmeric is highly recommended by Dr. Al Sears, M.D.
Recommended reading
https://alsearsmd.com/2016/09/turmeric-natures-miracle-root-for-disease/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NF-%CE%BAB
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inflammation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Turmeric
http://inflammationfactor.com/look-up-if-ratings/
http://www.theredheadriter.com/2012/08/anti-inflammatory-and-if-rating-healthy-diet-foods/
https://theconsciouslife.com/top-10-inflammatory-foods-to-avoid.htm
Science references
https://academic.oup.com/carcin/article-abstract/39/3/503/4830875?redirectedFrom=fulltext
http://pipelinereview.com/index.php/2018022867489/DNA-RNA-and-Cells/AnGes-Announces-First-Patient-Treated-with-NF-kappa-B-Decoy-in-Phase-Ib-Study-to-Treat-Discogenic-Low-Back-Pain.html
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2777480/
More on Dr. Ranjan Sen
https://gradimmunology.med.som.jhmi.edu/faculty/sen_r.html
https://irp.nih.gov/pi/ranjan-sen
http://www.bio.brandeis.edu/faculty/sen/Sen_Symposium_2016_FINAL.pdf
Pictures are from wikipedia.org except Dr. Sen's picture is from nih.gov
You are welcome to comment, upvote and/or resteem.
Thank you for viewing.
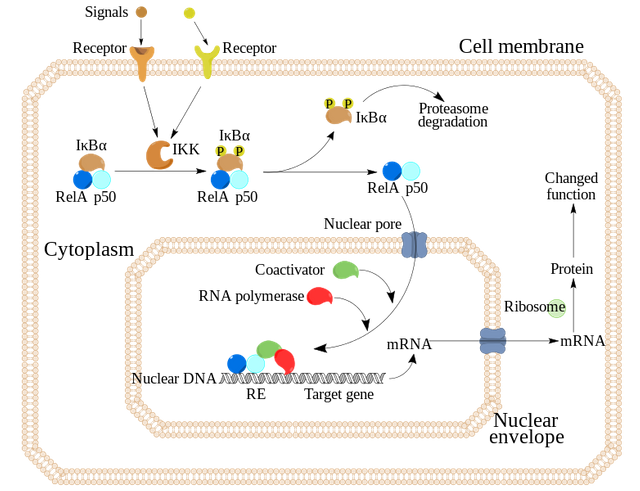
So, many different downstream pathways lead to formation of an IKK complex which then phosphorylates IKb-a; which is bound to NF-κB in its inactive state. The phosphorylation leads cellular proteases to destroy the phosphorylated IKb-a, bonded to NF-κB. The IKb-a is bound to NF-κB when inactive. The phosphorylation allows the IKb-a to detach from NF-κB. The NF-κB (alone, now) can now enter the nucleus and bind to DNA. NF-κB transcribes mRNA which is then translated, making inflammatory proteins, furthering inflammation .
Side note: Doesn't aspirin work by inhibiting IKb-b (NSAID) which stops COX production?
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Wow, you're very knowledgeable. Thank you for your insight.
As for your question, from what I've read, aspirin irreversibly inhibits COX-1 and modifies the enzymatic activity of COX-2.
COX-1 is involved in pain, promoting clotting, and protecting the stomach
COX-2 is involved in the pain produced by inflammation
COX-2 inhibitors (not aspirin) are effective against inflammation and avoid damage to the GI tract, but they increase the risk of blood clots.
AnGes, Inc. is doing a 12 month study injecting a NF-kB Decoy directly into the intervertebral discs of patients with chronic discogenic low back pain (DLBP). Hopefully without the problems of COX inhibitors, but it will most likely come with new side effects.
More info on all this here:
If your target is inflammation in the arteries, Nitric Oxide derived from L-arginine supplementation can be very effective. Some are much better than others. I personally like the chocolate chewables CardioForLife at https://www.healthguardian.com/product/name/cardioforlife/id/1930190
More info about nitric oxide here:
OOOOPS... My answer got a bit too long and off topic. I need to go now. Thanks again for your comment.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I cant remember if Nitric Oxide has more binding affinity to a hemoglobin molecule than oxygen. I believe it does something funky to a bound oxygen/ hemoglobin. I believe NO can work as an antioxidant, removing superoxidants producing peroxynitrites. And if not enough endothelium produced NO can lead to peroxide formation so its amount must be in homeostasis. In this way it eases oxygen transport, too. Sorry, I dont know too much else. Im unsure how NO effects immunity.
thanks for the COX info, btw. I love your post and will follow in the future!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you for the compliment.
I don't know which has a higher binding affinity, but I do know that it is very important for hemoglobin to pick up some NO (nitric oxide) in the large arteries to be released, along with oxygen, in the tiny peripheral arteries.
NO is the smooth muscle "relaxing factor". For every blood pulse from the heart, NO is released by the endothelium growing on the inside surface of our arteries. Some of the NO goes through the artery wall and into the nitrergic neurons on tense smooth muscle surrounding the arteries causing the smooth muscle to relax so the arteries can dilate for every blood pulse.
Some of the NO gets picked up by hemoglobin in the red blood cells to be released when passing through the tiny peripheral arteries because tiny peripheral arteries have no endothelium to make NO. Every artery, big or small, will not dilate without enough NO.
As the NO passes from the endothelial cells through any plaque build up and through the artery wall, it dissolves the plaque and cleans the arteries.
In immunity, macrophages engulf (phagocytosis) bacteria and then use NO to help kill the bacteria.
NO is a major player in many biological processes and a fascinating molecule.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Good job on the article. I'm not to clued up on Biology, however this is interesting.
My go to natural ingredient is ginger, make a nice hot cup of tea with grated ginger. It's actually quite spicy.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Yes, ginger is a good anti-inflammatory.
Thanks for your nice compliment.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit