In a science report that may come as a form of relief to cancer patients undergoing treatment and people who are genetically prone to have cancer; a University of Texas research into ancient enzymes and biopsies is about to change how cancer cells can be detected quickly and profiled in the body.
Professor Alan Lambowitz of the Institute for Cellular and Molecular Biology and the Department of Molecular Biosciences, in the University of Texas, and his team of scientists are studying an ancient enzyme in bacteria which can be used to detect genetic materials shed by cancer cells, or bits of other diseased cells that are released into the bloodstream of a patient.
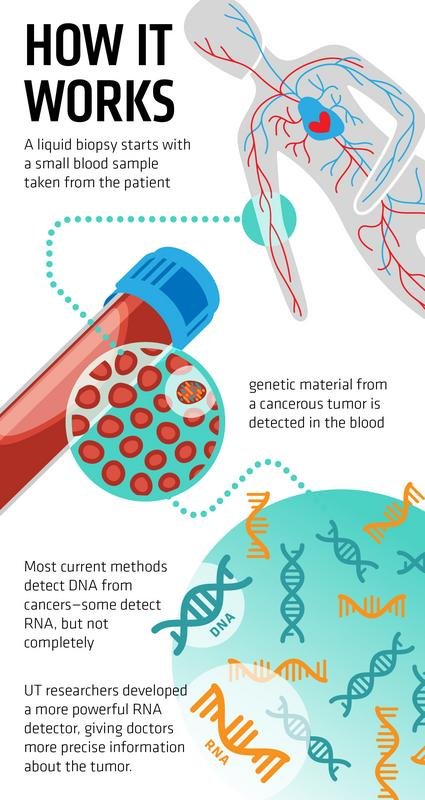
The research by the scientists is geared towards developing a set of medical tests termed ‘liquid biopsies’. These forms of biopsies are said to have the potential to rapidly detect infectious diseases in the body, presence of cancer and other medical conditions, from just a small sample of blood.
The project by the researchers at the Texas University is part of a new tool being developed which could provide doctors with more details about a patient’s disease.
Unlike surgical biopsies which are normally associated with long waits; the new tool called liquid biopsies would aid prompt and early detection thereby improving the chances the individual has of finding the best treatment, as well as sparing the person the pain and inconvenience synonymous with surgical biopsies.
What are biopsies?
Various medical journals and professionals define biopsy in different ways, but common definitions include;
A biopsy is commonly performed as a medical test, by an interventional cardiologist, a surgeon, or an interventional radiologist, and it involves the extraction of sample cells or tissues for close examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease.
A biopsy is also define as a sample of tissue taken from the body in order to examine it more closely. A doctor should recommend a biopsy test for a patient when an initial test suggests that an area of tissue in the body isn't normal.
How do liquid Biopsy Work?
There are liquid biopsies which currently exist today. Some of them can detect DNA in the blood. Some others can detect RNA. But the current liquid biopsies often miss many key RNA bio-markers and even misinterpret others.
But the ancient enzyme being described in a paper published recently in the Molecular Cell journal, has the ability to detect the full range of RNA’s with a high level of accuracy. This improved quality of the ancient enzyme would be helpful in understanding diseases, including the general profile of cancer diseases and also provide specific details about the disease’s activity within a particular patient system.
Without a doubt, this improved method could provide a key tool enabling doctors to pursue the field of precision medicine, unique aspect of diseases and treatments which are based on the genetics and life histories of the affected individuals.
The Research and Study
During the course of the new study, the molecular structure of this RNA-detecting enzyme was uncovered in action, by Jennifer Stamos a postdoctoral researcher. The discovery offered clues as to how the enzyme would work and how it can be used for further medical test applications.
DNAs and RNAs present in all living cells contain genetic details which are useful in understanding the state of a disease such as cancer, in the body.
The DNA which is found mainly in the nucleus of the cell is like a restaurant’s menu which contains all the information regarding the meals available for a customer to choose from. While, the RNA found mainly in the cytoplasm of the cell – although still synthesized in the nucleus – is like a customer’s order citing the quantity and types of meals requested.
According to Professor Alan Lambowitz;
“DNA biomarkers are static. They provide information about mutations that cause a disease, but they don’t provide information about the effect of these mutations on cellular processes, which can differ in different individuals,” said Lambowitz.
The limitation of the DNA marker is one of the reasons why a cancer-causing mutation can have varying effects on the individual, and also lead to different response to treatment.
Professor Lambowitz further said that;
By contrast, “Monitoring cellular RNAs provides a snapshot of exactly what is happening in diseased tissue, such as a tumor, at a particular time.”
“The method can be used to monitor day-to-day progression of the disease and response to treatment and to predict how different individuals with the same cancer will respond to different treatments.”
The Ancient Bacterial Enzyme, GsI-IIC RT
Professor Alan Lambowitz alongside his team believe that this ancient enzyme called Gsl-IIC RT and some TGIRT group of enzymes, possess properties which make it easier to detect and profile RNA biomarkers observed from cancer cells and other disorders.
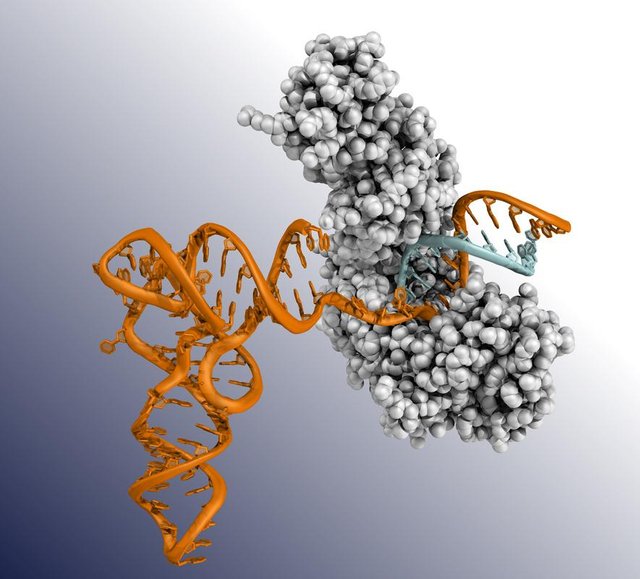
An ancient bacterial enzyme (grey colour) is seen crawling along a tangled strand of RNA (orange colour), thus creating a complimentary strand of DNA (blue colour). |
|
Benefits of the GsI-IIC RT – ancient enzyme
Prof Lambowitz foresees a liquid biopsy method that when combined with other tools would provide a whole lot of information to health professionals.
Lambowitz studies the TGIRTs group of enzymes which he believes can help massively with cancer detection. TGIRTs helps to uncover RNA strands and then creates a complimentary strand of DNA to match it - this encodes the same information, and can be sequenced rapidly to reveal diagnostic information.
Prof Lambowitz also believes that because the TGIRTs can accurately make DNA copies of almost any type of RNA using very small starting materials, they would be better when it comes to catching biomarkers for diseases, unlike the currently available RNA-based liquid biopsies.
Tests and Trials
Currently, Professor Lambowitz with his team are working together with clinicians to carry out tests on the liquid biopsies based on the TGIRT (ancient) enzyme.
One particular test and trial study going on at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston is focused on inflammatory breast cancer.
A second trial phase at the City of Hope National Medical Center near Los Angeles is focused on multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma is a type form of cancer which affects the bone marrow.
Once the tests are confirmed successful, the new liquid biopsies would be applied together with other liquid biopsy techniques which are currently in use, such as the one which detects biomarkers of chromosomal abnormalities in a developing fetus of pregnant mothers, through their blood study.
Approval and Patents
Co-author to the research study is Alfred Lentzsch. He is a molecular biosciences graduate. The study of the TGIRTs enzyme was supported by the Welch Foundation and the National Institutes of Health.
Professor Lambowitz and the Texas University are minority equity holders in InGex, a University of Texas spin-off company licensed with the patents and patent applications subject of the TGIRTs enzymes, as well as the method of their use.
Lambowitz, some of his present and former lab members, along with the University of Texas receive royalty payments generated from the sale and distribution of TGIRT enzymes, the kits and the intellectual property license.
In conclusion
The TGIRTs are ancient enzymes which date back to the period when genetic information were stored mainly in RNA. But then, life was gradually transitioning to DNA.
The new study further showed that TGIRT enzymes are very similar to enzymes which come from RNA viruses and which copy the RNA. The study highlights the evolutionary role the TGIRTs ancient enzyme would play in the evolution of present day organisms that depend on DNA for genetic materials.
Source/Reference: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Thank you for your time and for reading my post.
If you found this post interesting, then kindly UPVOTE, RESTEEM and FOLLOW @rickie, for more quality posts.

excellent post which is quite educational. liquid biopsy? wow! what a find and with such mankind will be better off as regards cancer detection and management!
thanks for sharing
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Yes @kenhudoy. Mankind would be better off with very prompt detection of cancer cells, in the hope combating them early. Thanks for visiting and reading through!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Welcome as always and keep it coming. ! Do so find time to check some of my blog posts
Regards
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
When cancer is genetic, why is it in nearly each family? Why do about 80% of the 80 year old have at least an early version of thyroid cancer?
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Genetic ? Obesity RUNS in my family
NO
The problem is nobody RUNS in your family ;)
What runs in the family ?
Lifestyles
Habits
Bad food choices
Drugs
Vaccines
Smoking
Exercise
Etc
Not saying yours just what I see
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
A big food for thought! Nice one
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Found this theory worth thinking about. In short: severe sugar metabolism failure would cause deadly wave of strokes. The tumor sucks up the sugar, fixing the acute problem while bein deadly long-term.
«The tumor is clearing the excess glucose from the blood and replacing it with an abundance of lactate to provide usable fuel for the critical organs like the heart and the brain. This is one reason why the tumor is part of the solution instead of part of the problem»
https://www.westonaprice.org/health-topics/modern-diseases/cancer-to-the-rescue/
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hmm. Serious issue...food for thought indeed...
Which is why I mainly blog on waste to wealth. Take a look...!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Am so elated seeing this unusual post on health,will like to see more
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks @hydrolife
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
excellence post indeed, with this i can just read this print as my project topic in my school if only my lecturer will accept it
good work
upvoted and resteemed
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks @solowire. Goodluck with your school project.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Amen
if my lecturer approve it ill tell you and congratulate you
please don't give up health post please i really do enjoyed it because that's my field
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
IMO biopsy can puncture a tumor that was encapsulated
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Conventional treatment does not kill the Cancer stem cells only the daughter cells, daughter cells make up the bulk of the tumor .
Kill the queen bee kill the hive if not cancer can survive .
So was the treatment effective ? Tumor shrunk BUT cancer is back .
We need to target the cancer stem cells ;)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
With cancer IMO very important to understand Krebs cycle and Glycolysis.
The Mitochondrial play an important role
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I really don't like to sit when the talk is about cancer so I will pass.... I wan go chop like that!
😂😂😂😂👏👏👏👏👏
But you tried the post is longer than those ancient scroll, it must have taken you 18 months, 3 weeks, four days and 17 hours to put this together. I guess the geeks would find this enjoyable.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit