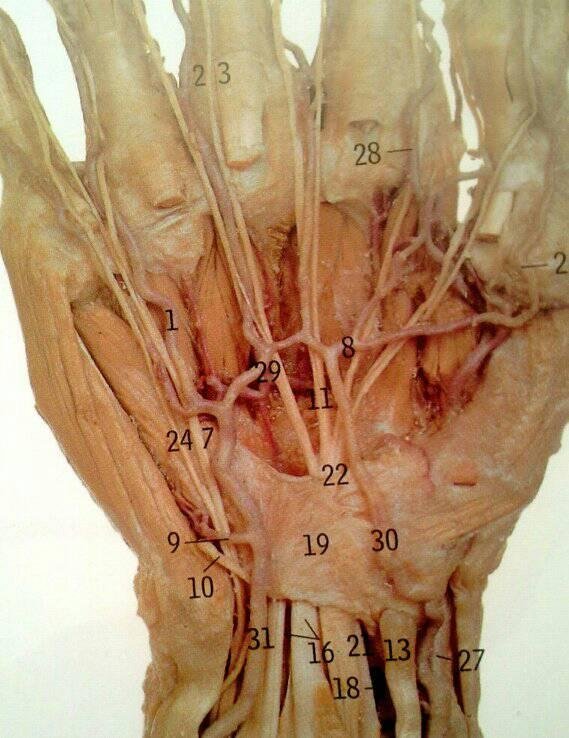
Fuente de imagen: Gran Atlas de anatomía humana McMinn.
Síndrome del túnel carpiano.
El túnel del carpo es un espacio ubicado a nivel del miembro superior en la región anterior de la muñeca, en la profundidad del tendón del musculo Palmaris longus. Está formado por un espacio virtual constituído por los huesos: Os Pisiforme, Os Scaphoideum , Os Hamatum y Os Trapezium. Dicho espacio se encuentra cubierto por el ligamento transverso del carpo, y contiene en su interior: los tendones Flexor Digitorum (profundus y superficialis) de los dedos, Flexor Pollicis Longus, y el nervio mediano.
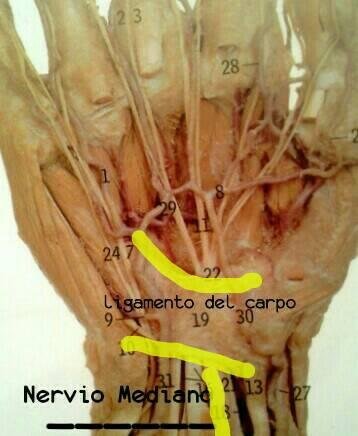
Fuente de imagen: Gran Atlas de anatomía humana McMinn.
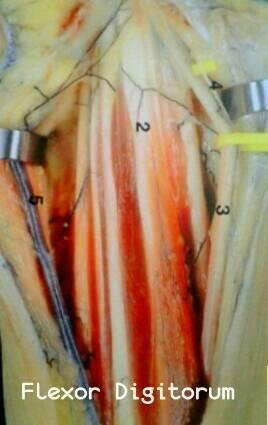
Fuente de imagen: Personal.
El síndrome del túnel carpiano, es un cuadro clínico el cual obedece a la compresión del nervio mediano en su paso por esta región, se produce en 0,1 al 10% de la población general, no obstante, afecta principalmente a mujeres a partir de los 40 años. Existen factores de riesgo tales como: obesidad, hipotiroidismo, diabetes, embarazo, tabaquismo, ocupación, postraumáticos, etc., sin embargo en el 95% de los casos las causas son idiopáticas.
Clínica.
• Dolor y parestesias a predominio nocturno (calambres, sensación de hormigueo) en mano y dedos.
• Pérdida de la fuerza en la mano.
• Atrofia muscular, en casos avanzados.
Diagnóstico.
Existen algunas maniobras que permiten diagnosticar este cuadro, entre ellas:
• Maniobra de Phalen: dorsiflexión de muñecas durante 1 minuto aproximadamente, se considera positiva si el paciente refiere dolor o parestesias.
• Signo de Tinel: se percute a nivel del ligamento transverso del carpo y si existe compresión, se manifiesta sensación de “corrientazo” a lo largo de la muñeca y mano.
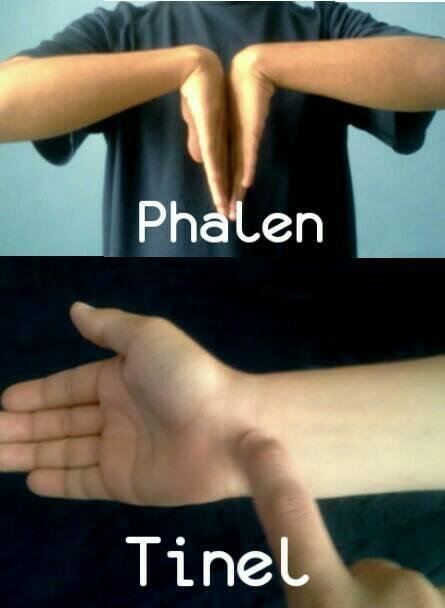
Fuente de Imagen: Personal.
•La Electromiografía: consiste en la medición de la velocidad de la conducción nerviosa del miembro superior afectado.
Tratamiento.
- Debe tratarse la causa de base.
- Cambio de hábitos.
- Tratamientos paliativos: inmovilización con férulas, infiltración con anestésicos y corticoesteroides locales.
Realmente estos recursos solo ofrecen mejoría transitoria en menos de un 80%, para luego recidivar, por lo tanto, el tratamiento debe ser quirúrgico a través de un procedimiento conocido como Neuroadhesiolísis el cual consiste en la liberación del ligamento transverso del carpo y de esa manera se descomprime el nervio mediano. Es una cirugía en teoría muy rápida de 15 a 20 minutos, se utiliza anestesia local, con una incisión minima en la región volar (anterior) de la muñeca, de 3 cms. Aproximadamente.
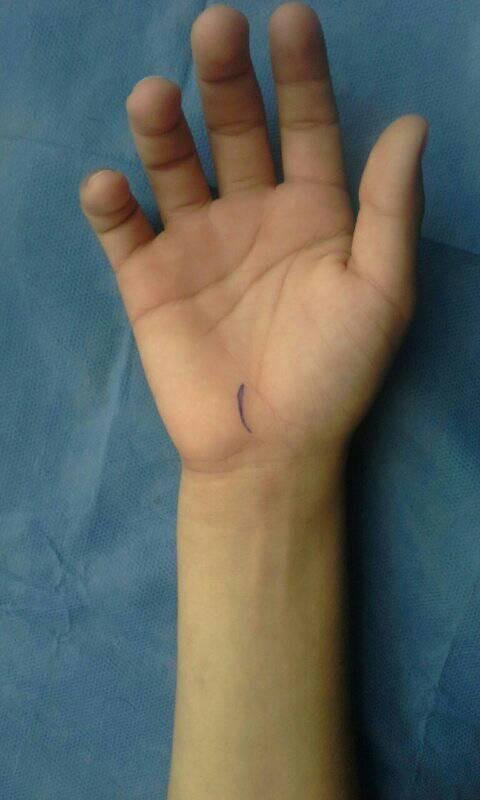
Fuente de Imagen: Personal.
También se realiza por vía endoscópica, no obstante, algunos autores defienden la técnica convencional abierta ya que reduce el riesgo de una liberación incompleta con la consecuente recidiva.
Se inicia la movilización inmediata de la muñeca, con precaución, claro está.
Dentro de las complicaciones más frecuentes destacan:
Persistencia de las manifestaciones clínicas (por liberación incompleta del ligamento).
Pillar Pain: la herida postquirúrgica se retrae generando dolor local o por lesión de nervios sensitivos (más frecuente en incisiones transversas).
Infecciones de la herida.
Lesión iatrogénica del nervio mediano.
Como en toda entidad patológica, es recomendable tener un diagnóstico certero antes de proceder a cualquier
conducta y de esa manera garantizar el éxito en la evolución del paciente.
Referencias Bibliográficas.
-Exploración física de columna vertebral y las extremidades, Stanley Hoppenfeld. Ed. El Manual Moderno.
-Anatomía descriptiva L. Testut-A. Latarjet. Elsevier España, S.L.
-Cirugía Ortopédica y Traumatología A.D. Delgado Martínez. Ed. Médica Panamericana.
Carpal tunnel syndrome.
The carpal tunnel is a space located at the level of the upper limb in the anterior region of the wrist, in the depth of the Palmaris longus muscle tendon. It is formed by a virtual space constituted by the bones: Os Pisiforme, Os Scaphoideum, Os Hamatum and Os Trapezium. This space is covered by the transverse carpal ligament, and contains in its interior: Flexor Digitorum tendons (profundus and superficialis) of the fingers, Flexor Pollicis Longus, and the median nerve.
The carpal tunnel syndrome is a clinical entity which obeys to the compression of the median nerve in its passage through this region, it occurs in 0.1 to 10% of the general population, however, it mainly affects women from 40 years old. There are risk factors such as: obesity, hypothyroidism, diabetes, pregnancy, smoking, occupation, post-traumatic, etc., however in 95% of cases the causes are idiopathic.
Clinic.
• Pain and paresthesias predominantly at night (cramps, tingling sensation) in the hand and fingers.
• Loss of strength in the hand.
• Muscular atrophy, in advanced cases.
Diagnosis.
There are some maneuvers that allow to diagnose this picture, among them:
•Phalen maneuver: dorsiflexion of wrists for approximately 1 minute, it is considered positive if the patient refers pain or paresthesias.
• Tinel's sign: it is felt at the level of the transverse carpal ligament and if there is compression, a sensation of "electric shock" is manifested along the wrist and hand.
• Electromyography: is the measurement of the nerve conduction velocity of the affected upper limb.
Treatment.
- The underlying cause must be treated.
- Change of habits.
- Palliative treatments: immobilization with splints, infiltration with anesthetics and local corticosteroids.
Actually these resources only offer transient improvement in less than 80%, then relapse, therefore, the treatment must be surgical through a procedure known as Neuroadhesiolysis which consists of the release of the transverse carpal ligament and thus the median nerve is decompressed. It is a very fast surgery in theory from 15 to 20 minutes, local anesthesia is used, with a minimum incision in the volar (anterior) region of the wrist, of 3 cms. approximately.
It is also performed endoscopically, however, some authors defend the open conventional technique as it reduces the risk of incomplete release with the consequent recurrence.
Immediate mobilization of the wrist , with caution, of course.
Among the most frequent complications include:
Persistence of clinical manifestations (due to incomplete release of the ligament).
Pillar Pain: post-surgical wound retracts generating local pain or injury of sensitive nerves (more frequent in transverse incisions).
Infections of the wound.
Iatrogenic injury of the median nerve.
As in any pathological entity, it is advisable to have an accurate diagnosis before proceeding to any behavior and in this way guarantee success in the patient's evolution.
Bibliographic references.
-Exploración física de columna vertebral y las extremidades, Stanley Hoppenfeld. Ed. El Manual Moderno.
-Anatomía descriptiva L. Testut-A. Latarjet. Elsevier España, S.L.
-Cirugía Ortopédica y Traumatología A.D. Delgado Martínez. Ed. Médica Panamericana.
Sindrome del tunnel carpale.
Il tunnel carpale è uno spazio situato a livello dell'arto superiore nella regione anteriore del polso, nella profondità del tendine del muscolo lungo Palmaris. È formato da uno spazio virtuale costituito dalle ossa: Os Pisiforme, Os Scaphoideum, Os Hamatum e Os Trapezium. Questo spazio è coperto dal legamento carpale trasverso e contiene al suo interno: i tendini del Flexor Digitorum (profundus e superficialis) delle dita, Flexor Pollicis Longus e il nervo mediano.
La sindrome del tunnel carpale è un'entità clinica che obbedisce alla compressione del nervo mediano nel suo passaggio attraverso questa regione, si verifica nello 0,1-10% della popolazione generale, tuttavia colpisce principalmente le donne di 40 anni. Ci sono fattori di rischio come: obesità, ipotiroidismo, diabete, gravidanza, fumo, occupazione, post-traumatico, ecc., Tuttavia nel 95% dei casi le cause sono idiopatiche.
Clinica.
• Dolore e parestesie prevalentemente notturne (crampi, sensazione di formicolio) nella mano e nelle dita.
• Perdita di forza nella mano.
• Atrofia muscolare, nei casi avanzati.
Diagnosi.
Ci sono alcune manovre che permettono di diagnosticare questa immagine, tra queste:
• Manovra di Phalen: dorsiflessione dei polsi per circa 1 minuto, è considerata positiva se il paziente riferisce dolore o parestesie.
• Il segno di Tinel: si avverte a livello del legamento carpale trasverso e se vi è compressione, si manifesta una sensazione di "shock elettrico" lungo il polso e la mano.
• Elettromiografia: è la misurazione della velocità di conduzione nervosa dell'arto superiore interessato.
Trattamento.
- La causa sottostante deve essere trattata.
- Cambiamento di abitudini.
- Trattamenti palliativi: immobilizzazione con stecche, infiltrazione con anestetici e corticosteroidi locali.
In realtà queste risorse offrono solo miglioramenti transitori in meno dell'80%, quindi ricadono, pertanto, il trattamento deve essere chirurgico attraverso una procedura nota come Neuroadesiolisi che consiste nel rilascio del legamento carpale trasverso e quindi il nervo mediano viene decompresso. È un intervento chirurgico molto veloce in teoria da 15 a 20 minuti, viene utilizzata l'anestesia locale, con un'incisione minima nella regione del volare (anteriore) del polso, di 3 cm. circa.
Viene anche eseguito endoscopicamente, tuttavia, alcuni autori difendono la tecnica convenzionale aperta in quanto riduce il rischio di rilascio incompleto con la conseguente recidiva.
Immediata mobilizzazione del polso, con cautela, ovviamente.
Tra le complicazioni più frequenti includono:
Persistenza delle manifestazioni cliniche (a causa del rilascio incompleto del legamento).
Dolore alla colonna: la ferita post-chirurgica si ritrae generando dolore o lesione locale dei nervi sensibili (più frequente nelle incisioni trasversali).
Infezioni della ferita.
Lesione iatrogena del nervo mediano.
Come in qualsiasi entità patologica, è consigliabile avere una diagnosi accurata prima di procedere a qualsiasi comportamento e in questo modo garantire il successo nell'evoluzione del paziente.
Riferimenti bibliografici.
-Exploración física de columna vertebral y las extremidades, Stanley Hoppenfeld. Ed. El Manual Moderno.
-Anatomía descriptiva L. Testut-A. Latarjet. Elsevier España, S.L.
-Cirugía Ortopédica y Traumatología A.D. Delgado Martínez. Ed. Médica Panamericana.
Hi dear @soanna
Thats a great post
Best of luck dear
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hi! thank you! enjoy it!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @soanna! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDownvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Ciao Soanna! Hai ricevuto il voto del trail di @steemit-italia!
Entra nel nostro server discord per ricevere tutti i nostri benefici e seguire le nostre iniziative!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Ciao! Grazie per il vostro voto, mi auguro vi serva!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulazioni!
Hai appena ricevuto il voto del trail di @steemit-italia***
Se vuoi, puoi informarti sul nostro progetto qui e partecipare anche tu al trail, ottenendo il beneficio di poter ricevere gratuitamente il voto sui tuoi post una volta al giorno!Clicca sul banner per entrare sul nostro server discord!
Delega a Steemit-Italia: 50SP |100 SP |500 SP| 1000 SP
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Excelente información.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Gracias! espero te sirva de ayuda. saludos!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Saludos, amiga gran información y muy interesante.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Saludos! muchas gracias, espero haya sido de tu utilidad!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Vaya, bastante interesante este contenido, no conocia mucho sobre este sindrome.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Gracias Christian!, esto es apenas un resumen del cuadro clínico.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @soanna! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDownvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit