Good evening friends of steemit today
I will talk a little about The Organism, let's know more about our bodies through this information.
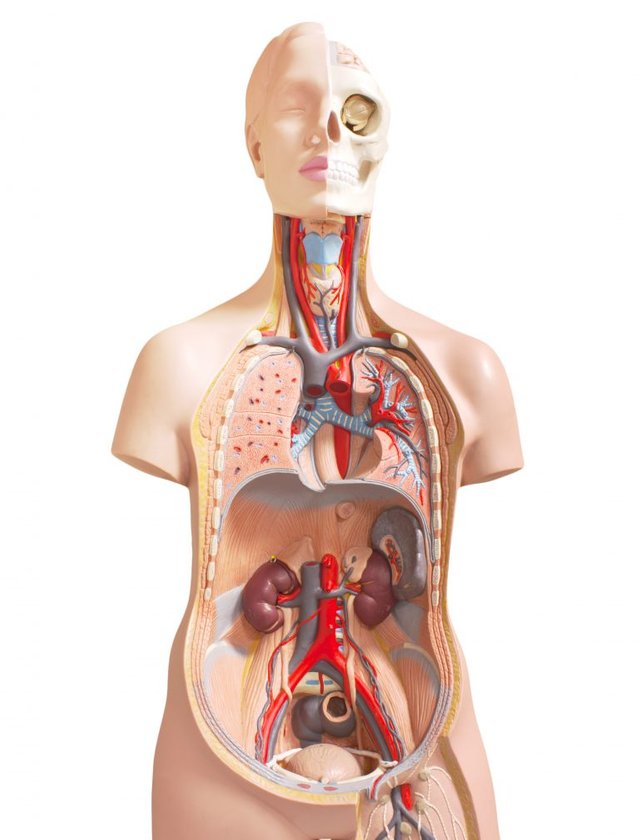
The organism
the whole body Leather is organized into five different levels of increasing complexity: from cells to, through tissues, organs and systems. The tissues are formed by the grouping of similar cells, and two or more tissues form an organ, such as the stomach or the heart. The organs and tissues that collaborate with each other to perform a bodily function (such as digestion) give rise to the 12 systems of the body. These do not operate in isolation but depend on one another to keep the body functioning.
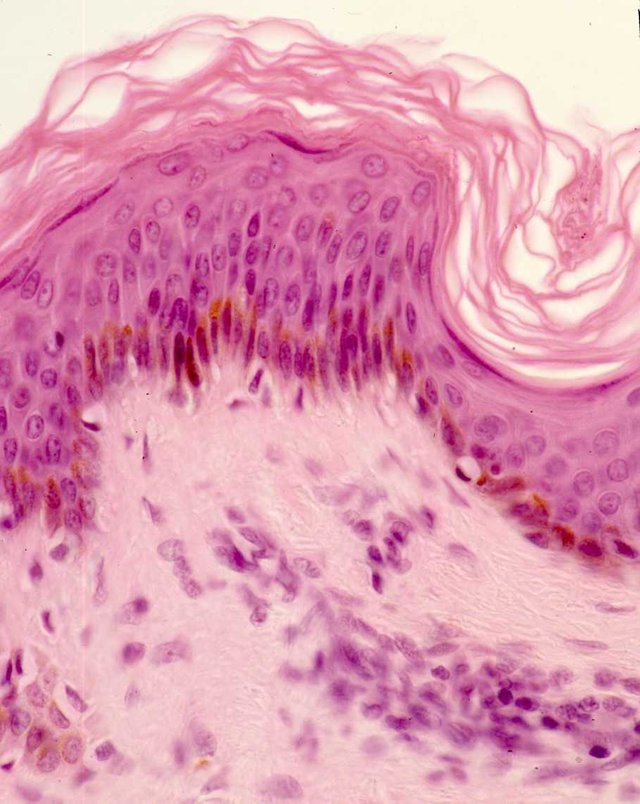
Epithelial tissue
The epithelial tissue, or epithelium, covers and protects the body and its hollow organs and cavities. In the image we see the epithelium that covers the trachea. It consists of a mantle of cells very aretaron to each other, that form a barrier against the invading microorganisms. The epithelial cells are continually divided to replace those that have worn away.
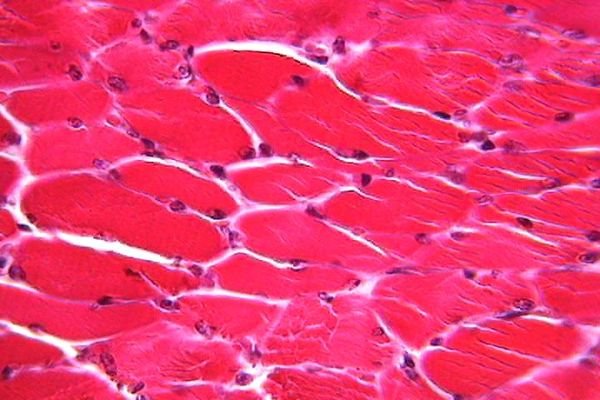
muscle tissue
Muscle tissue cells, called fibers, contract under the stimulus of nerve signals. The skeletal muscle that we see here moves the body. It has long striated fibers and adheres to the skeleton. The cardiac muscle, exclusive of the heart, pumps blood throughout the body. In the wall of the hollow organs the muscle is smooth and changes shape.
Conjunctive tissue
This is the most diversified of all tissues. It forms a structure that supports, protects and isolates the body and gives it cohesion. In cartilage and in bone, as well as in tendons and ligations, there are various conjunctive tissues. The collagen fibers we see here give strength and flexibility to connective tissues. Other types of these are adipose tissue and blood.
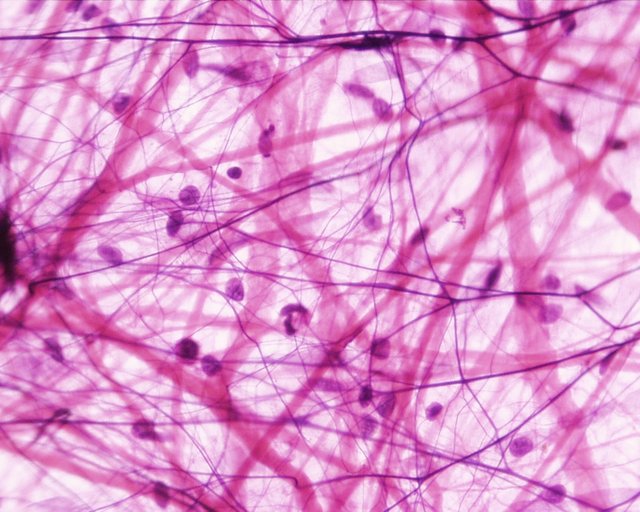
Nervous tissue
The largest communication and control network of the body (brain, spinal cord and nerves) is formed of nervous tissue. This is made up of nerve cells, or neurons, that transmit electrical signals (nerve impulses), and gliable cells that support neurons. We see a section of nervous tissue in the cerebellum, a part of the brain that coordinates movement.

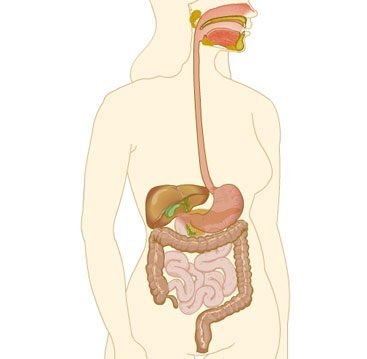
Digestive device
This absorbs and processes the food for what the body takes advantage of. Like other devices, it is made up of linked organs that work together. For example, the esophagus impels the food already swallowed to the stomach, where it converts it into a liquid mass.
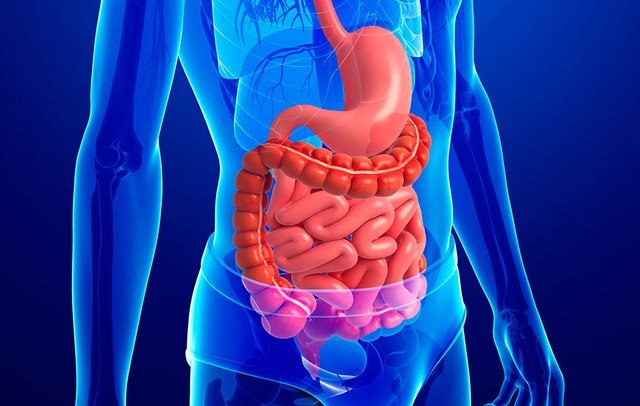
Organ-stomach
In the digestive system, the stomach stores the swallowed food and directs it in part. Like other organs (such as the kidneys of the urinary system), its shape is identifiable and consists of several tissues. Some of these allow the stomach to contract; others give him blood or nervous stimuli, or, they cover him internally.
tissue-mucosa
Cross section of the folded cover of the frame, seen with a microscope: the mucosa or mucous membrane is formed by three of the types of tissue that make up that organ. The surface is covered by a thin layer of epithelium. Below this is a thicker layer of connective tissue, on the smooth muscle layer of the mucosa.
Epithelial cells
Micrograph of the surface of the cells of the epithelium that covers the stomach. The tight junctions between the cells prevent the corrosive gastric juices from reaching the connective tissue below, and also secrete mucus, which covers and protects the cells. The cells surround the entrance to the gastric gland, which secretes the gastric juices.