Hello friends, welcome at my third post of food chemistry! Today I decided to write about ice cream which is a mixture of milk, cream, sweeteners, stabilizers, emulsifiers, flavouring agents, pigments and starch hydrolysates. The caloric value and nutrients of ice cream depend on the quality and nutritional value of the raw materials used.
The total energy value of ice cream depends on:
- the percentage of carbohydrates including lactose,added sweeteners, raising agents, sugars found in fruits and milk proteins,
- the percentage of fat from any source e.g. eggs, cocoa, nuts and more.
Milk proteins contained in ice cream are of excellent biological value because they contain all the essential amino acids needed in the human body. Caseins account for about 80% of milk proteins and consist of α1-caseins, α2-caseins, b-caseins and k-caseins. The major proteins belonging to the group of serum proteins are: b-galactoglobulin, a-galactoglobulin, immunoglobulins and serum albumin. Milk proteins are important sources of tryptophan and lysine. In addition, they are better absorbed by the body than other proteins. The protein content can be calculated by determining the nitrogen contained in the food by the Kjeldahl method, Dumas or similar methods.
Milk fat consists mainly of triglycerides of fatty acids. Triglycerides are glycerol esters linked to fatty acids. In milk, there are about 400 fatty acids and contains about 11.8 and 4.6 moles of butyric and hexanic acid, respectively, per 100 moles of total fatty acids. Milk fat also contains 2.25% diacylglycerol, 1.11% phospholipids, 0.46% cholesterol, 0.28% free fatty acids, and 0.08% monoglycerides. Milk fat contains a relatively low content of polyunsaturated fatty acids (about 4.5%), but contains about 27% of monounsaturated fatty acids.
The carbohydrates present in ice cream are starch, dextrin, cellulose, sugars, pectins and others. There are many types of sugars that can be used to make ice cream. The most common sugar used is sucrose, a disaccharide consisting of a molecule of glucose and a fructose molecule. Invertebrate is also used which is a mixture of glucose and fructose and is derived from the hydrolysis of sucrose. In addition, corn syrup, derived from hydrolysis of starch, can also be used in ice cream and replacing a portion of sucrose.
Lactose is a sugar of milk and a disaccharide consisting of a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule. It accounts for 20% of the carbohydrate in the ice cream.
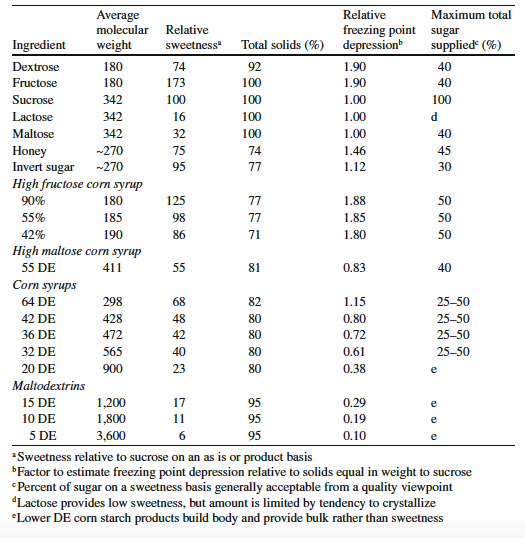
Sweetness can vary greatly from one sugar to another. For example, fructose is sweeter than sucrose. In the table below we see the relative sweetness of various sugars.
Another set of ingredients used in making ice cream are the stabilizers. The stabilizers are usually polysaccharides and their main purpose is to immobilize the water and in this way bring the following desirable features to the ice cream:
- Increase the viscosity of the mixture.
- Improve structure and texture.
- Improve air incorporation.
- Do not allow large ice crystals to appear.
- Stabilize proteins by reacting with them.
- Improve the ice cream properties during melting.
- Retain the ice cream structure by preventing the loss of volume.
Emulsifiers are substances with a hydrophilic and a lipophilic pole. They are compounds that allow the interaction of fats and water, and thus allow the dispersion of the lipids in aqueous solution. Emulsifiers are used in small quantities that should not exceed 2% but their contribution to a product is particularly high because:
- Prevent the emergence of large ice crystals in ice cream.
- Improve the dispersion and good distribution of liposomes in the mixture and the texture of the ice cream improves.
- Homogeneity is offered to the mass of the product giving a smooth texture to the ice cream.
- Hold in the water.
- Facilitate fat-protein reactions.
- Improve the properties of ice cream when it is melted.
- Retain the ice cream structure, resisting their loss of volume.
- Ice cream shows dry and does not stick to walls when leaving the freezer.
- Contribute to the aggregation of the liposomes and facilitate the incorporation of air.
The most commonly used substances in mixtures are guar and locust bean gum (LBGs), cellulose gum, carrageenan (hydrocolloid), mono / diglycerides, sugar esters, sorbitan fatty esters and polysorbate 80 (emulsifier). Gelatin can also be used as an ice cream stabilizer. However, the ice cream industry has incorporated more sophisticated methods of stabilizing and emulsifying from the use of gelatine for both operational and economic reasons.

Whether in the confectioner's small lab or in a large industry. the basic stages in making ice cream are the same.
- Preparation of ingredients - weighing of raw and auxiliary materials
- Pasteurization - Mixing mixture: The materials are brought to special machines and with simultaneous stirring and heating we achieve the dispersion and mixing of the ingedients, as well as the thermal decontamination of the mixture.
- Homogenize the mixture for better homogeneity and texture of the product.
- Refrigeration and maturation: after homogenization, the mixture is instantly cooled (for microbial purposes) and stays in special tanks for 24 or 48 hours, at 2-4 ° C, where they bind the components together.
- Freezing - swelling: after maturation, the mixture is frozen at -4, -5 ° C, with simultaneous introduction of air. This embodiment results in an increase in volume of 50 to 120% of the original volume and gives the ice cream its foam composition.
- Packing-tempering: After freezing and inserting the air, the ice cream is packaged in containers and remains in special freezing chambers at -40 ° C, where it takes its final form and then is stored in freezing and distributed.
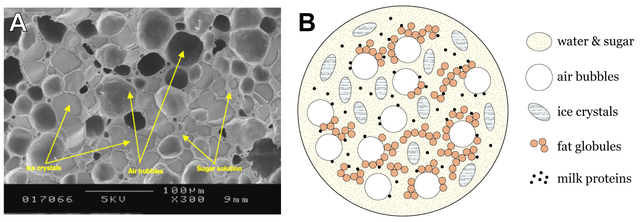
Although at first glance the ice cream seems simple in its composition, its structure is quite complicated. With a closer look, we see a structure that could be described as a mixture of ice crystals and air bubbles trapped in a network of non-frozen sugar solution. The non-frozen sugar solution results from the freezing because at the drop of temperature, water is transferred from the aqueous solution to ice crystals while concentrating it and increasing the concentration of sugars in the non-frozen phase. The structure of the ice cream is determined by the proportions of the three different elements, namely ice, air, and the non-icy grid.
Let's look at the element of ice, the most important element of ice cream. The liquid water becomes ice at about 0 ° C, and we know that ice cream is consumed at temperatures between -14 and -10 ° C. If the ice cream had only water, then we would have a solid product, hard and difficult to consume. So, the amount of ice it contains should be controlled and a part of the water must stay wet. This can be done by lowering the freezing point of water below 0 ° C, which is done by adding various ingredients such as sugars, salts and alcohol.
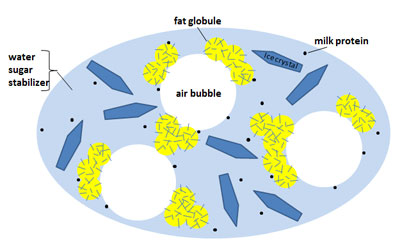
So we understand the so complex physical and chemical changes that need to be achieved to come up with a product that will come out on the market and be acceptable and safe for the consumer. Through this research and testing framework every year, the industry presents new types and new flavors to attract and satisfy the consumer.
References
wikipedia
scienceandfooducla
icecreamscience
icecreamscience
icecreamscience
icecreamscience
icecreamscience
icecreamscience
Thanks for reading!!If you liked my post upvote, resteem, or follow @zkalemiss for more...
ICE CREAM is Life! Thanks for writing such an informed article so others can learn what makes up ice cream's compound. Although it may not be as healthy as fruits and veggies there are a few great benefits to it.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Great Post! Keep up this kind of work. :-)
It was a nice refresher of what I heared last semester. 🤗
Best,
mountain.phil28
PS: If you are interested in some more and other chemical-physical topics have a look at my Blog. ;-)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Yummy and nice explanation
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Very nice post. Do take out sometime and follow my blog and share some feedback on my posts as well.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit