Addiction can be defined as a chronic longing for something or an activity which you have little or no control over. Addiction is a serious problem in the society today a we have over 80% of our youths suffering from one addiction or the other.
Often times, when we hear the word addiction, the first thing that comes to mind is the use and abuse of drugs or the ingestion of chemical substances which we get addicted to but drugs isn’t the only addiction harmful to man.
There’s is a popular saying that goes, ‘’ too much if everything is bad’’. Meaning that one can actually be addicted to virtually anything and once you get addicted to something, it becomes harmful to you.
Do you disagree with this? Ok, think of any harmless thing you could possibly get addicted to. Getting addicted to it and doing it out of proportion can indeed turn to become harmful or bad for your health, physically or psychologically.
Now, what’s the science behind addiction…
The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and white matter sits at the center of all human activity—you need it to do and enjoy virtually all your everyday activities. In brief, the brain regulates your body’s basic functions; enables you to interpret and respond to everything you experience; and shapes your thoughts, emotions, and behavior.
The brain is made up of many parts that all work together as a team. Different parts of the brain are responsible for coordinating and performing specific functions. Addiction can alter important brain areas that are necessary for life-sustaining functions. Brain areas affected by drug abuse include:
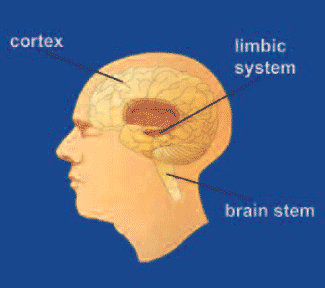
image source
• The brain stem: which controls basic functions critical to life, such as heart rate, breathing, and sleeping.
• The cerebral cortex: which is divided into areas that control specific functions. Different areas process information from our senses, enabling us to see, feel, hear, and taste. The front part of the cortex, the frontal cortex or forebrain, is the thinking center of the brain; it powers our ability to think, plan, solve problems, and make decisions.
• The limbic system: which contains the brain’s reward circuit. It links together a number of brain structures that control and regulate our ability to feel pleasure. Feeling pleasure motivates us to repeat behaviors that are critical to our existence. The limbic system is activated by healthy, life-sustaining activities such as eating and socializing—but it is also activated by addiction to a substance or anything.
In addition, the limbic system is responsible for our perception of other emotions, both positive and negative, which explains the mood-altering properties of many addictions where by you feel strongly the urge to do that which you are addicted to and just seconds after you’ve done it, you feel this guilt within you which makes you feel like never doing it again but hey, it’s an addiction and so you see yourself going back to it over and over again.
How does the parts of the brain communicate?
Knowing how the brain communicate with its cells to give certain responses would help us know the effect addiction has on the brain and how the brain responds to addiction.
The brain is a communications center consisting of billions of neurons, or nerve cells. Networks of neurons pass messages back and forth among different structures within the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves in the rest of the body.
These various communications occur as follows;
• Neuron to Neuron
Each nerve cell in the brain sends and receives messages in the form of electrical and chemical signals. Once a cell receives and processes a message, it sends it on to other neurons.
• Neurotransmitters - The Brain's Chemical Messengers
The messages are typically carried between neurons by chemicals called neurotransmitters.
• Receptors - The Brain's Chemical Receivers
The neurotransmitter attaches to a specialized site on the receiving neuron called a receptor. A neurotransmitter and its receptor operate like a “key and lock,” an exquisitely specific mechanism that ensures that each receptor will forward the appropriate message only after interacting with the right kind of neurotransmitter.
• Transporters - The Brain's Chemical Recyclers
Located on the neuron that releases the neurotransmitter, transporters recycle these neurotransmitters (that is, bring them back into the neuron that released them), thereby shutting off the signal between neurons.
Now I think this might seem a bit complex to some of you who are probably not biologists and so below is a diagram to help you picture what actually goes on in the brain when it comes to communication and interaction between the neurons and receptors in the brain.
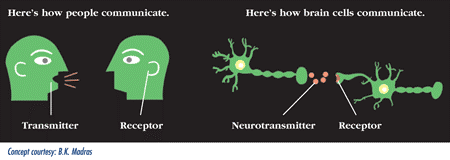
image source
To send a message, a brain cell (neuron) releases a chemical (neurotransmitter) into the space (synapse) between it and the next cell. The neurotransmitter crosses the synapse and attaches to proteins (receptors) on the receiving brain cell. This causes changes in the receiving cell showing that the message has been received.
I am sure this is now crystal clear as we now know how the brain communicates. Now how does this apply to addiction?
How does addiction work in the brain?
Addictions are like chemicals that affect the brain by tapping into its communication system and interfering with the way neurons normally send, receive, and process information. Some addictions, such as addiction to marijuana and heroin, can activate neurons because their chemical structure mimics that of a natural neurotransmitter.
This similarity in structure “fools” the receptors and allows the drugs to attach onto and activate the neurons. Although these drugs mimic the brain’s own chemicals, they don’t activate neurons in the same way as a natural neurotransmitter, and they lead to abnormal messages being transmitted through the network.
How does addiction work in the brain to produce pleasure?
Addictions target the brain’s reward system by flooding the circuit with dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter present in regions of the brain that regulate movement, emotion, motivation, and feelings of pleasure. When activated at normal levels, this system rewards our natural behaviors such as the urge to drink water, sleep, eat or laugh.
Overstimulating the system with drugs, substances or a particular constantly attributed behaviour however, produces euphoric effects, teaching the user or individual to repeat it and that’s why we find ourselves going back to things we are addicted to over and over again.
Is addiction a brain disease?
Now many would be interested in knowing if someone who is addicted to something, has some kind of brain disease. The answer is YES. If you doubt this, then we can take out a little time to analyse addiction as it relates to being a brain disease.
A disease is a condition that changes the way an organ functions. Addiction does this to the brain, changing the brain on a physiological level. It literally alters the way the brain works, rewiring its fundamental structure. That’s why scientists say addiction is a disease.
Do you know why now? Owk lets continue…
Although there is no cure for addiction, there are many evidence-based treatments that are effective at managing the illness. Like all chronic illnesses, addiction requires ongoing management that may include medication, therapy, and lifestyle change. Once in recovery from addict The first time a person tries alcohol or another drug, it’s a voluntary choice. But at some point during use, a switch gets flipped within the brain and the decision to use is no longer voluntary.
Anyone who tries a substance or decides to live a particular lifestyle can become addicted.
After initial exposure, no one chooses how their brain will react to the use of a substance or to exposure to a particular lifestyle. So why do some people develop addiction, while others don’t? There are three basic factors responsible for this and they are;
• Genetics
Scientific research has shown that 50–75% of the likelihood that a person will develop addiction comes from genetics, or a family history of the illness. Exactly how genetics factor into addiction, and what we could do to protect against their influence, is something scientists are actively researching right now.
• Environment
Research shows that growing up in an environment with older adults who use drugs or engage in criminal behavior is a risk factor for addiction. Protective factors like a stable home environment and supportive school are all proven to reduce the risk.
• Development
Addiction can develop at any age. But research shows that the earlier in life a person tries a substance or becomes exposed to a particular lifestyle, the more likely that person is to develop addiction. Our brains aren’t finished developing until we’re in our mid-20s. Introducing such substance to the brain or getting exposed to that kind of lifestyle during this time of growth and change can cause serious, long-lasting damage due to addiction.
How to prevent addiction
Of cause, it can. Before we begin to look at the preventive measures to take, we have to first analyse and be aware of the risk factors. Reducing these risk factors and increasing protective measures would definitely help curb addiction in the society. What are these risk factors? The risk factors are those factors that contribute to the need to get addicted to something. Below is a table that shows the risk factors with the aim of making you aware of them and so try to prevent them which will in turn help prevent the advent of addiction.
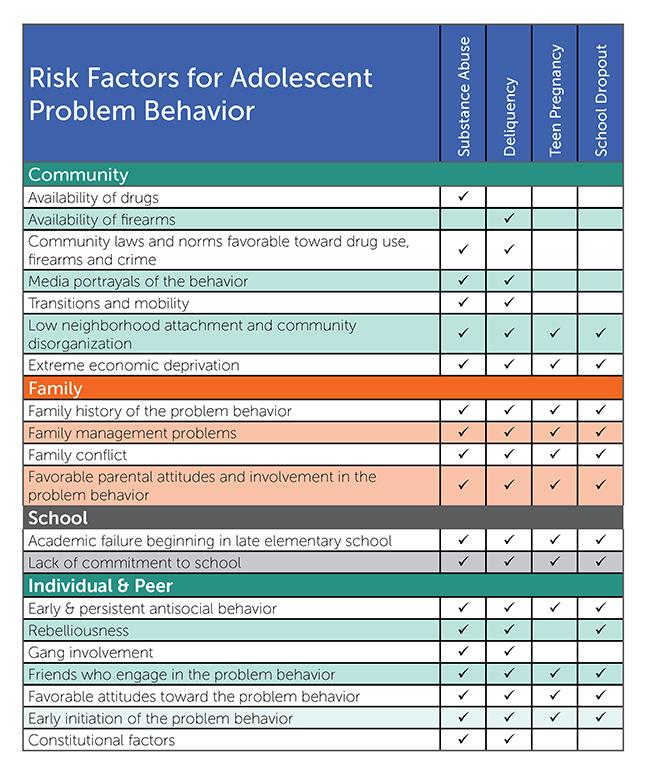
image source
Can addiction be treated?
Since it has been established that addiction is a disease and like most diseases, it can be treated. The first step to treating an addiction is the realization that you are addicted. Once you’ve realised tat yo are addicted, then you can use any of the following methods to stop your addiction;
• Stay away from lonely places
• Chose the right company
• Visit a psychologist
• Hang around people who have the same addiction and are willing to stop it. Team work would make you stop your addiction faster.
• Never be found around r close to whatever you are addicted to.
• Finally, pray pray pray…prayer still works wonders.
IN CONCLUSION
Addiction is not a moral failing…
Addiction is not a choice. It’s not a moral failing, or a character flaw, or something that “bad people” do. Most scientists and experts agree that it’s a disease that is caused by biology, environment, and other factors.
Harmful consequences, shame, and punishment are simply not effective ways to end addiction. A person can’t undo the damage addiction have done to their brain through sheer will power and so we need to show them love and help them overcome their addiction and with that, we get to rid our society of every form of addiction.

Very interesting article.
I found this time locker very helpful: https://steemit.com/addiction/@niel96/p3g8rhdww
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Here's a video comparing a healthy brain to someone with an addiction. It shows changes in different regions of the brain.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This is very comprehensive.. You just got a follow... I love your analysis of the science behind addiction...
Keep up the good work @steemnaira
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Very nice!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Well analysed and very informative.
Kudos to you.
You just got a resteem...
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Great post!
But guess what?
Am addicted to steemit
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Addiction is a very serious challenge in society today.
Most youths in my locality have taken to recreation drugs for fun, but have ended up as addicts.
Sadly, the society see it as a moral & social ill but beyond that is a serious health challenge that needs the concerted effort of friends, family, social & health workers and governments to solve.
@steemnaira thanks for sharing this timeous piece.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Nice try but largely full of plagiarized contents. Learn to us > if you want to quote somebody else's work word for word.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
All of us have an addiction. Some are addicted to drugs, alcohol or smoking. Other are addicted to computer games, social media or television. Reminding yourself that too much of your addiction can be bad for you will help you control it.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit