Stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood flow to the brain is interrupted or reduced. The lack of oxygen and nutrients can cause damage to the brain cells, leading to long-term disability or death. According to the World Health Organization, stroke is the second leading cause of death and the third leading cause of disability worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss everything you need to know about stroke, including its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
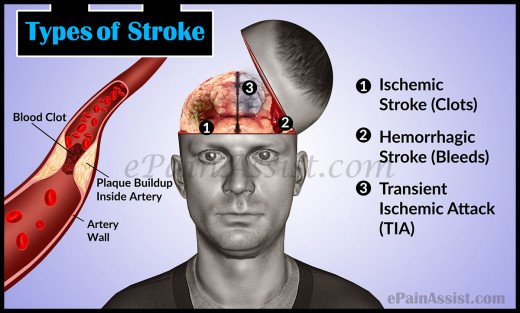
Types of Stroke
There are two main types of stroke: ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic Stroke
Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, accounting for about 87% of all strokes. It occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the arteries that supply blood to the brain, blocking the flow of blood and oxygen. The clot can form either in the brain or in another part of the body and travel to the brain through the bloodstream, causing a blockage in a smaller artery. Ischemic strokes can also occur due to atherosclerosis, a condition in which the arteries become narrow and hard due to the buildup of plaque.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is a less common but more severe type of stroke, accounting for about 13% of all strokes. It occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding and damage to brain tissue. Hemorrhagic strokes can be caused by an aneurysm, a weakened and bulging section of a blood vessel, or by high blood pressure, which can weaken the blood vessel walls and make them more prone to rupture.
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
Transient ischemic attack (TIA), also known as a "mini-stroke," is a temporary interruption of blood flow to the brain. The symptoms of a TIA are similar to those of a stroke but usually last for a shorter time, usually a few minutes to a few hours. TIAs are often warning signs of an impending stroke and should be taken seriously.
Strokes are usually caused by a combination of risk factors, including:
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is the most common risk factor for stroke. When the blood pressure is high, it can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of a stroke.
Smoking
Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots, making it a major risk factor for stroke.
Diabetes
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of atherosclerosis, making it a significant risk factor for stroke.
High Cholesterol
High cholesterol can cause the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can increase the risk of atherosclerosis and stroke.
Obesity
Obesity can increase the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, all of which can increase the risk of stroke.
Age
The risk of stroke increases with age, with the risk doubling for each decade after the age of 55.
Gender
Men are more likely to have a stroke than women, but women have a higher risk of death from stroke.
Family History
A family history of stroke or other cardiovascular diseases can increase the risk of stroke.
The symptoms of a stroke can vary depending on the type and severity of the stroke. The most common symptoms of stroke include:
1.Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
2.Sudden difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
3.Sudden confusion or trouble with vision, such as blurred or double vision
4.Sudden severe headache with no known cause
5.Sudden dizziness or loss of balance or coordination
These symptoms usually occur suddenly and without warning.
