*** Whole tone & Half tone (Curtains and half curtains) ***
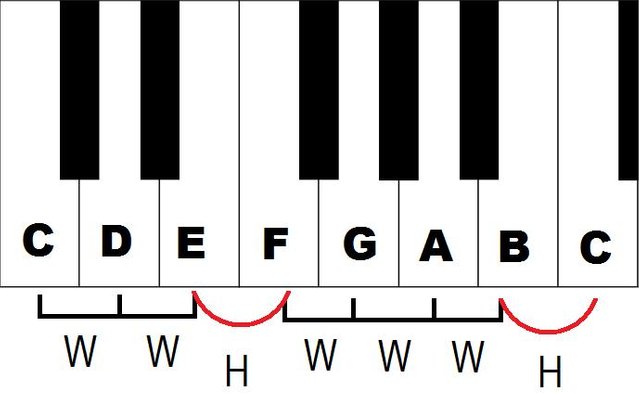
The unit curtain measures physical distances in music. As in daily life, we use units such as meters and centimeters to measure distances, and music is also used to measure distances from the curtain and half curtain. The definition of the curtain in each instrument is different, for example, in a piano from any white key until the next white key is a curtain, and from any white key until the next black key is half the curtain, or in the guitar from each fret up the next half and up to 2 frit The next is a curtain.
There are two types of halves in the music: the first half of the diagonal curtain and the second half of the curtain chromatic.
Diatonic Blind:
This half-curve is the distance between two sequences of non-named names, and in the natural pattern, diatonic steps can be seen, and can occur with both modifier signs and alternate signs.
Chromatic halves:
This half-curtain is the distance between two notes, and at least one of its notes is either Dais or Baml.
Comma:
The smallest unit of distance measurement is called Comma, when we divide a curtain into nine equal parts, each part is called a coma.
Octave:
The largest distance measurement unit in Octave music is called Otave, each octet consists of 5 shades and 2 halves and always ends with the name of the originator.
One quarter of Micro Tones:
A quarter of a curtain is smaller than half a curtain, and is usually seen in Iranian and Middle Eastern music.
In the example below, the intervals between the notes are displayed in an octave. Note that these distances are common in all instruments.
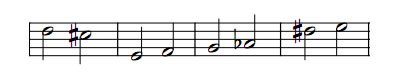

.jpg)