Some gas turbine power plants take advantage of the excess air by means of a multistage turbine with a reheat combustor between the stages. With this arrangement the net work per unit of mass flow can be increased. Let us consider reheat from the vantage point of an air-standard analysis. The basic features of a two-stage gas turbine with reheat are brought out by considering an ideal air-standard Brayton cycle modifiel. After expansion from state 3 to state a in the first turbine, the gas is reheated at constant pressure from state a to state b. The expansion is then completed in the second turbine from state b to state 4.
The ideal Brayton cycle without reheat, 1–2–3–4'–1, is shown on the same T–s diagram for comparison. Because lines of constant pressure on a T–s diagram diverge slightly with increasing entropy, the total work of the twostage turbine is greater than that of a single expansion from state 3 to state 4'.
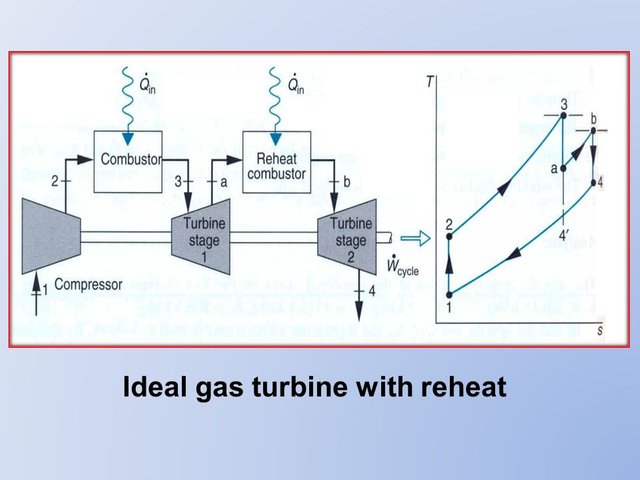
Thus, the net work for the reheat cycle is greater than that of the cycle without reheat. Despite the increase in net work with reheat, the cycle thermal efficiency would not necessarily increase because a greater total heat addition would be required. However, the temperature at the exit of the turbine is higher with reheat than without reheat, so the potential for regeneration is enhanced.
Engineering Model:
- Each component of the power plant is analyzed as a control volume at steady state.
- The compressor and turbine processes are isentropic.
- There are no pressure drops for flow through the heat exchangers.
- The regenerator effectiveness is 100%.
- Kinetic and potential energy effects are negligible.
- The working fluid is air modeled as an ideal gas.