Trade sits in between the supply and the demand and tries to match the quantities on both sides. Collaborative economy introduces platforms as match makers. Looking back in time eBay and Craiglist are the pioneers of the platform oriented economy, both have very different business models, but both acquaints individuals to the market and vice versa. While eBay had the whole process of purchasing, payment and delivery rounded up, Craiglist only served as a bulletin board and later on this bulletin board became inspiration for the raising collaborative platforms. Both Craiglist and eBay have great impact on the development of collaborative economy.
Most of the ideas of the today’s collaborative platforms originated from Craiglist,
and most of the collaborative platforms use reputation systems which eBay introduced as a mechanism for measuring success and trustworthiness in the trading process.
Match making is all about trust.
Collaborative economy being a process of two complete strangers trading goods for money required a mean for identifying individual trustworthiness. Reputation systems became a tool for articulating trust through the individual’s past activities and by building individual reputation. Collaborative economy needed trust as any other human interaction does, including the economic one, so the reputation systems together with the customer reviews became the backbone of the collaborative economy.Loosing trust was the first thing that was mentioned when one looks at the consequences of the economic crisis from 2007–2009. People needed to put themselves on the market for new types of economic interactions, both as suppliers and as consumers and those new interactions required new forms of trust. The socio-economic entities, that were previously guarantors for these interactions were now out of the picture, so the newly established trust among individually took over. Below we can see how the recommendation from people and consumer opinions have the biggest percentage of trust among all other ways of influencing peoples decisions.
This mentioned a 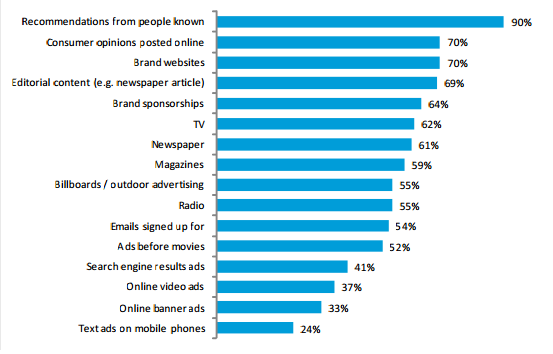
This mentioned and having in mind the drop in the institutional trust, as in banks, (see below)
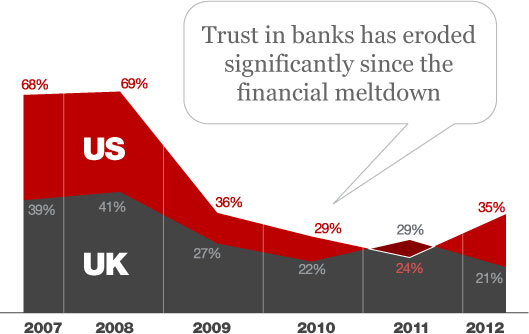
and the emerging trust in the ICT sector (see below) gives the collaborative economy’s combo of people + technology a big competitive advantage over the old industries.
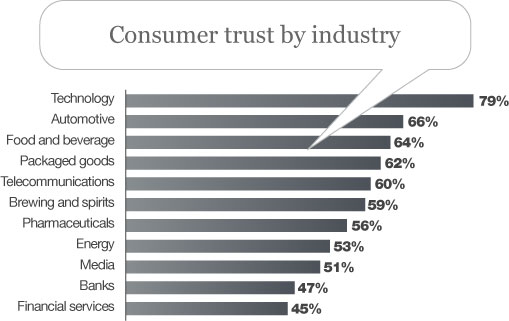
The shift in trust towards people and towards the ICT industry brings out another question. If people can produce and consume by themselves and can trade through ICT solutions and if this whole ecosystem is showing considerable results, what happens to the old types of organizations like companies, banks etc.?
Platforms reduce transaction costs and administrate trust.
In the article “The nature of the Firm” Ronald Coase (1937) talks about the incentive behind the emerging of the companies as an economical and organizational entity. In short, companies emerged because they reduced the transaction costs of doing business. And what are transaction costs?
According to Dahlman, (put in his paper “The Problem of Externality” ,1979) there are 3 types of transaction costs:
- Costs for acquiring information — does the thing we are looking for exists on the market, where can it be found at lowest price etc.
- Costs for negotiating — finding common ground between the supplier and the consumer.
- Cost for ensuring the trade — legal matters, obligations etc.
Just by looking at this division of transaction costs we can pretty much correlate all of the above with the platforms that are supporting the collaborative economy. Platforms give us everything we should know about prices, availability and legal meters, together with the additional information from the community through the customer reviews and reputation systems about the trustworthiness of the entities involved. Having said this, it turns out that collaborative economy is not just disrupting the particular industries it also disrupts the concepts behind those industries i.e the corporate organizing. Certainly these are the extremes we are talking about, but extremes should be detected and should be put on a spotlight and by doing so the whole spectrum of opportunities that lies in between the extremes will be revealed and considered.
Reputation systems can be hacked, labor can be manipulated, platforms can be bad.
But, nothing is perfect. Being the pillar of the collaborative economy trust and reputation systems are on the very brink of the defense and it is a subject of manipulation and attacks in many different ways. People fake reputation by creating multiple profiles to simulate reputation, people give false rates on services just because they’ve been rated themselves, there are companies that do virtual make overs of one’s activities just to raise their reputation in the community etc. Reputation systems will be the most hacked endpoints as collaborative economy gains strength and validity.
As for the platforms, there is a big debate about the way platforms are using people’s resources to make profit for themselves. It is true that the final product is cheaper for the consumers, brings additional revenues to the suppliers and are environmentally friendlier, but there are concerns in the direction of labor rights, insurance, amortization etc. At this point the emergence of the trend and the shifts in capital is what matters with significant work to be done in the direction of regulations and competition.Gainers. Society got enriched, diverged and most of all it became aware of its potentials and the potential of the individuals. Suppliers and consumers gained platforms for trading and reduced the transaction costs in doing business. ICT sector entered new markets and new industries through the platforms, cutting off a significant portion of the profit from the old industries.Disrupted. Going so far as to question the necessity of companies and corporations means that the whole economic system is being fundamentally disrupted by the collaborative economy. Governments got disrupted as they must regulate new platforms and the new ways of doing business. Labor market also got disrupted as the platforms took a portion of company’s revenue and business i.e less labor will be needed. The part where technological innovations disrupts the labor market is not exclusive to platforms and collaborative economy, it is a phenomenon of every industrial revolution, in this case the digital age. Collaborative economy is maybe the most proportional in that manner, opening jobs for the self-employed as jobs are reduced in the corporate environments.
- the evolution of collaborative economy;
- supply, trade and demand aspects of the collaborative economy;
- the future effects collaborative economy will have on world economic processes;
- philosophical and economical concepts that can be perfectly mapped to the settings of collaborative economy;