Signal system no 7 is an architecture for out of band signalling which was developed in 1975. It is use to set up and tear down most of the world PSTN (Public Switching Telephone Network) telephone calls. It performs number translation and local number portability. It also performs prepaid billings, SMS (Short Message Services) and other message market services.
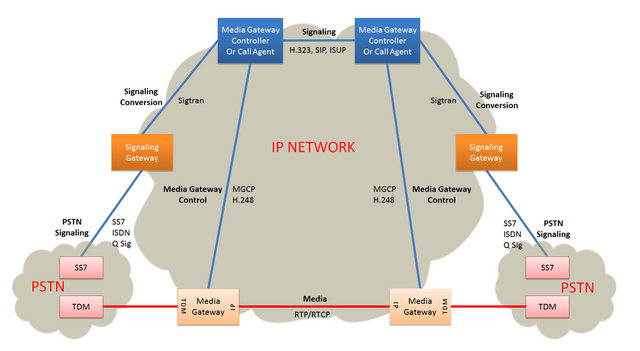
Signalling Gateway - SS7-IP interface, coordinates SS7 view of IP elements and Ip view of SS7 elements.
Media Gateway - Terminates PSTN lines and packetizes media streams for IP transport. Image source: Wikimedia
The term signalling here referes to the sharing of information between system components which are needed to maintain and deliver services. Here, the signalling links transmits information at the range of 56 to 64 kilobits/second.
Out of band signalling is when the signalling channel is different from the channel that carries the conversation. Its merit is that it allows signalling at any time during the entire duration of the call. It also permits transportation of more data at higher speed.
SS7 supports various application which include Public Switching Telephone Network (PSTN), Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN), Mobile Services and Administrative and maintenance operation of network. ISDN consists of collection of standards for communication for a successive digital transmission involving data, video and voice.. ISDN employs digital transmission from the customer’s premises equipment (CPE, example telephone, data terminals the machine etc.). Through the local access loop and access the carrier trunk network.
Components of ISDN include ISDN channels, Access type, Devices, Interfaces and Protocols. A channel is the basic unit of ISDN services. The ISDN standards define three basic types of channel they include: Bearer channel (B channel), Delta or demand Channel (D channel), High capacity channel (H channel).
B channel consists of a 64 kilobits/second units of digital bandwidth. B channel can carry any type of digital information (carries data or video) with no restriction on format or protocol imposed by the ISDN carrier. D channel is a signalling channel that carries the information needed to connect or disconnect calls and to negotiate special calling parameters (automatic number ID, call waiting, data protocols). Access D channel operates at 16Kbps and a primary rate access. D channel operates at 64Kbps.
H channel is a special high speed clear channel. It is designed basically for full motion colour video. We have H0 (H zero), H11 (H one one), H12 (H one two). H0 operates at 384Kbps, H11 operates at 1.536Mb (occupies a whole primary rate access), H12 occupies an entire European primary rate access.
))
A Network Termination for ISDN Basic rate Access. Image source: Wikimedia
ISDN Access type is of two types, Basic Rate access (BRA) and Primary Rate access (PRA).
Basic rate access is based on new technology conceived specifically for ISDN. Designed to provide service to individually users or small business. BRA provides two 64Kbps B channel and one 16Kbps D channel (referred to as 2B + D). It provides transmission facilities for one voice conversation (one B channel), one medium spared data session (the other B channel) and the signalling exchange needed to make them work (D channel). Adding two B channel at 64Kbps + D channel at 16Kbps = 144Kbps. The ISDN basic NAT transmission protocol uses an additional 48Kbps of bandwidth for maintenance and synchronization.
Primary rate access is based on the pre ISDN digital carrier technology. It is designed to provide high capacity service to large customer for application such as PBX to PBX trunking. There are two types of PRA: 23B + D and 30B+D
23B + D PRA operates at 1.544Mbps and offers 23B channel + 164Kbps D channel. 30B + D PRA operates at 2.148Mbps and offers 30B channel + 164Kbps D channel.
ISDN devices include Terminal Equipment (TE), Terminal Adapter (TA), Network Terminator 1(NT1), Network Terminator 2 (NT2) and Exchange Terminator (ET). Terminal equipment is a local device that speaks through an S interface. It can be directly connected to the network terminator 1 or network terminator 2 devices e.g. ISDN telephone and an ISDN fax. Terminal adapter connects TE2 devices to an ISDN. A TA connects through the R interface to the TE2 devices and through the S interface to the ISDN.
Network terminator is use to communicate directly with the central office switch. NT1 picks a connection of the type U from the telephone company and generates NT2 connection through a T interface. It handles the physical and electrical termination, line, monitoring and multiplexing.
SIGNALLING POINT
Signalling point in the SS7 network is identified uniquely by a numeric point code. Point code are used to identify the source and destination of individual message. We have three types of signalling point: Service Switching Point (SSP), Service Transfer Point (STP) and Service Control Point (SCP).
))
SS7 signalling point. Image source Wikimedia
SSPs are switches example class 5, class 4 (tandem) with SS7 interface. They convert global title digit from a subscriber line to SS7 signalling messages. They are switches that originates or terminate calls. SSPs send signalling messages to other SSPs to set up, manage and finally release voice circuit required to complete a call.
An SSP may also send query to a centralised data base to determine how to route a call. In summary, an SSP function is to use a global title to determine how to connect a call using its routing table.
STP is a router and or a gateway in the SS7 network, it provides traffic and usage measurement. It can act as a firewall to screen SS7 messages with other networks. STP switches SS7 messages between signalling point. If an originating SSP does not know the address of a destination SSP, the STP must provide it using global title translation.
SCP provides an application access. It is an interface to application such as database that provides information necessary for advance call processing capabilities. Service Control Point communicates with application using PRIMITIVES. Primitives is an interface that provides access from one level of a protocol to another level.
SIGNALLING LINKS
))
designed by @yandot using MS Word
In SS7 we have basically six types of signalling links: Type A, Type B, Type C, Type D, Type E and Type F. SS7 signalling links are characterised according to their users in the signalling network.
All signalling point are connected using pairs of links. Each link type is identified with a symbol as identified as shown on the right.
- TYPE A: Access
designed by @yandot using MS WordAn access link connects a signalling end point to an STP. Only messages originating from or destined to the signal end point on an A link.
- TYPE B: BRIDGE
designed by @yandot using MS WordA bridge link connects an STP to another STP. It basically connects an STP from one network to another STP in another network.
- Type C: Cross links
A cross link connects STPs performing identical function into a mated pair. A C link is only used when an STP has no other route available to a destination signalling point due to link failures.
- Type D: Diagonal links
A D link is use to connect paired STP at one level in the hierarchy to another level in the hierarchy. A D link connects a secondary (local or regional) STP pair to a primary STP in a quad link configuration. The destination between a D link or B link is rather arbitrary such links could be referred to as B|D links.
- Type E: Extended links
This type of link connects SSPs to alternate or remote STPs for increase in resilience and local sharing. It provides back up connectivity to the SS7 network in the event that the home STPs cannot be read through the A links. E links are very expensive.
- Type F: Fully Associated
This type of link is use to connect SSPs when significant traffic flow between them. It also connects two signalling end points.
References
- Signalling System No. 7 -Wikipedia
- ISDN protocols, components and router options -techtarget
- Point Code -Wikipedia
- Signalling System #7 General Overview -ss7net

))
))
You just got splashed by @rewards-pool. For more information on delegating to the @rewards-pool click the following link.
https://steemit.com/steemsilvergold/@rewards-pool/introduction-to-rewards-pool
@rewards-pool where a small delegation can get you a big splash.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Luar biasa pemaparannya Bang.
Maaf saya balasnya pakai bahasa Indonesia 😂
Di atas Abang juga menjelaskan tentang kekuatan pensinyalan. Ada H0 (H nol) H 11 dan H12
Ditempat saya sinyalnya H+, H+ masuk ke mana ya Bang? Ke H11 atau H12
Dijawab ya Bang @yandot yang baik hati 😊
Penasaran.
Terima kasih
salam hangat dari Aceh Jaya
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Membingungkan juga sih pertanyaannya ini karena tidak dijelaskan dalam sumber nya :D H11 dan H12 dimaksudkan untuk sinyal daerah eropa . Tapi sepertinya H+ mungkin masuk ke H11 karena tidak memiliki kecepatan terlalu tinggi di tempat kita :D
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hehehehe
Iya, terima kasih banyak @yandot untuk penjelasannya.
Sangat menarik.
BTW @yandot memang jurusan telkom ya?
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
you are sharing nice stuff here keep it up brother
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit