Sequence of events in the opening of the Afar region
The Suph rift (what today is the Red Sea), and the Turkana rift and Aden rift opened in the Oligocene, and extended by crustal rupture towards a focal point, to intersect in the Afar region. An older rift zone is found in the Persian rift, and the Tanganyika-Malawi rift, which was succeeded as the Gulf of Oman rift extended into the Persian rift, shifting the point of crustal rupture to the Suph-Turkana-Aden triple junction.
The image below shows the Persian-Tanganyika event in Eocene, which was later abandoned as Arabia separated from the middle east in the Oligocene, and the point of crustal rupture shifted to the Suph-Turkana-Aden rift.
Lake Victoria formed in the Oligocene as a basin between the Tanganyika-Malawi rift and the Turkana-Kenya rift.
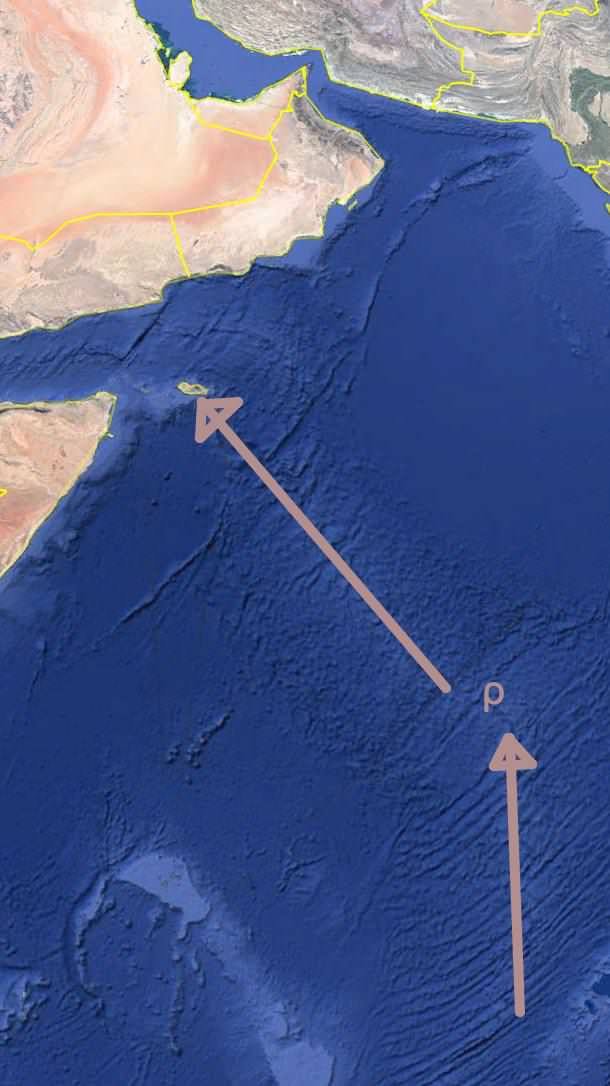
The image below shows the Suph-Turkana-Aden event, as a result of crustal rupture point having shifted as Afro-Arabia separated from the middle east.
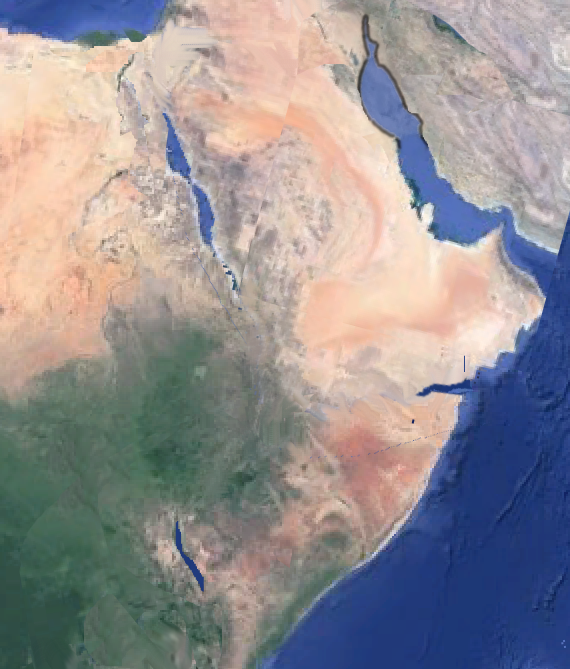

The Persian and Tanganyika-Malawi rifts approached a triple-junction with the Central Indian Rift. As the Gulf of Oman opened up and separated Afro-Arabia from the middle east, the tectonic focal point shifted to the Afar region, and the northward progression of the Central Indian Rift re-oriented (see point ρ in the image below) to form the Gulf of Aden.
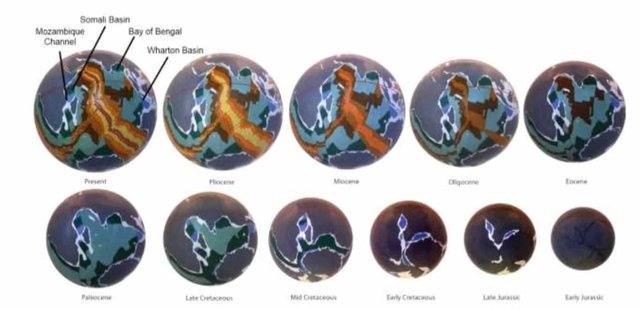
From the macro to the micro, comparing the opening of the Indian Ocean to the Afar triple junction
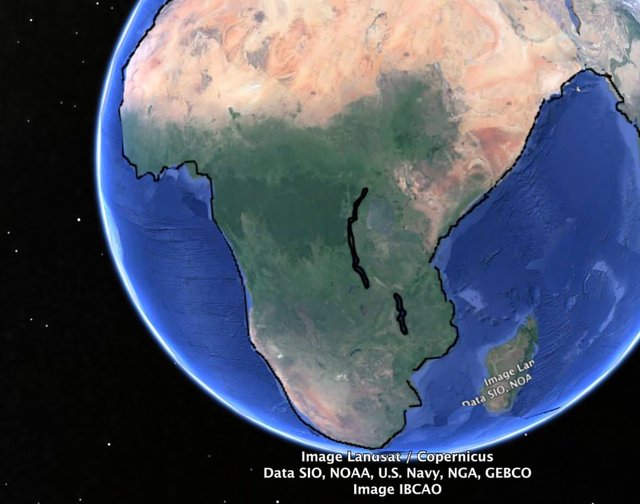
The Indian Ocean opened in the Jurassic, with three separate rift zones forming as a result of increase in earth radius, and crustal rupture. These three rifts, the Somali rift (in what is now the Somali Basin) to the west of India, the Bengal rift to the east (where the Bay of Bengal is today), and the Falkland rift to the south of Africa, then extended in the direction where there was least resistance, towards a focal point, to intersect and form a triple junction south of Madagascar.
Opening and a southward extension of the Somali rift continued up to the mid-Cretaceous Period into what later became the Mozambique Channel located between Madagascar and Africa, intersecting with the Bengal rift as well as the Falkland rift south of Madagascar. By the mid-Cretaceous Period, the Mozambique Channel spreading ridge was abandoned and a new spreading ridge commenced opening between Madagascar and India.
Once abandoned, the Somali Basin, Mozambique Channel, and Madagascar continent then remained as part of the African plate as seafloor crustal extension and opening progressively shifted to the east.
Expansion Tectonics and the history of ideas
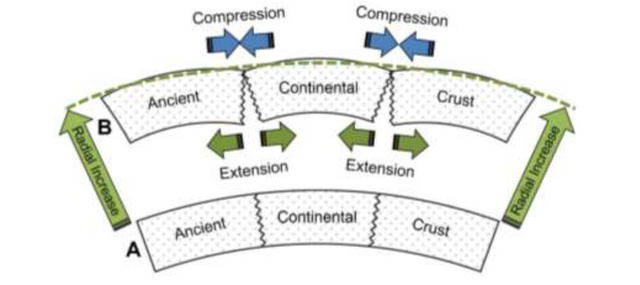
Within expansion tectonics, rift zones form from crustal rupture as a response to increase in earth radius.
The field of expansion tectonics has roots in Australia, a continent where it was close-to-heart to reflect on the position of Australia relative to the Pacific.
Root
On the Origin of Continents and Oceans- A Paradigm Shift in Understanding