What is thyroid cancer?
Thyroid gland, at the base of your neck, the butterfly-shaped thyroid gland is located just below your Adam's apple is seen in cells with a cloth . Thyroid hormones your heart rate, your blood pressure, body temperature, produces hormones that regulate your body weight.
Most cases of thyroid cancer can be cured with treatment.
What are the symptoms of thyroid cancer?
Thyroid cancer in the early stages of the disease typically any signs or does not sign. In later times, the following can result:
- A tuber that can be felt through the skin on your neck
- Progress in including hoarseness, changes in your voice
- Swallowing
- The pain in your neck and throat
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck
If you experience any of these signs or symptoms, make an appointment with your doctor. Thyroid cancer are not commonly seen, and therefore other causes of your signs and symptoms your doctor first investigate.
What are the causes of thyroid cancer?
The factors that lead to thyroid cancer are not fully understood. However, when the thyroid gland in your cells genetic change (mutations) occur. These mutations and allows rapid growth to the proliferation of the cells. At the same time, these cells, unlike normal cells, they lose the ability to die. Accumulated abnormal thyroid cells form a tumor. Abnormal cells can invade nearby tissues and can spread throughout the body.
What are the risk factors for thyroid cancer?
Factors that may increase the risk of thyroid cancer include the following:
- The female gender. Thyroid cancer is common in women than in men.
- High-level radiation exposure. High-level radiation exposure to the head and neck, or between instances of sources such as the fallout from weapons testing and nuclear power plant accidents radiation therapy facility.
- Certain inherited genetic syndromes. Genetic syndromes that increase the risk of thyroid cancer, familial multiple endocrine neoplasia type models and includes.
What are the complications of thyroid cancer?
Recurrent thyroid cancerEven the thyroid gland has been removed and may recur despite treatment. This is taken into the thyroid gland microscopic cancer cells before they spread beyond the thyroid can happen if.
Thyroid cancer can recur in the following areas:
- Lymph nodes in the neck
- During surgery small pieces of thyroid tissue that can be placed
- Other areas of the body
What can be done to prevent thyroid cancer?
Doctors, in most cases of thyroid cancer does not know the responsible factor and, therefore, there is no way to prevent thyroid cancer in people at average risk for this disease.Prevention for people at high risk
Anaplastic thyroid cancer thyroid cancer in children and adults with inherited gene mutations that increase the risk of surgery is often recommended to prevent (prophylactic thyroidectomy). Your options of thyroid cancer, consult with a genetic Counselor who can explain your risk and your treatment options.
Prevention in people who live near a nuclear power plant
Emitted as a result of an accident that occurred at the nuclear power plant Fallout, may cause thyroid problems in people who lived nearby. If you live within 10 miles of a nuclear power plant, a drug that blocks the effects of radiation on the thyroid (potassium iodide) it may be appropriate to take. If an emergency were to occur, you and your family, you can take potassium iodide tablets to help prevent thyroid problems. For more information, consult your doctor.
Thyroid cancer is diagnosed how?
Thyroid Biopsy
Tests and procedures used to diagnose thyroid cancer include the following:
- Physical Examination. Take care of your physical changes with your doctor thyroid and excessive radiation exposure, and family history will ask your risk factors for thyroid cancer.
- Blood tests. Blood tests helps determine whether the normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
- A sample of thyroid tissue to be taken. Your doctor during a fine needle biopsy, a long, thin needle thyroid nodules extends to the inside of your skin. Precise advancement of the needle within the nodule is typically used for ultrasound imaging. Suspicious thyroid tissue samples to get your doctor to inject this uses. This sample will be analyzed in a laboratory to look for cancer cells.
- Imaging tests. Your cancer has spread beyond the thyroid gland your doctor to help you determine whether you can get one or more imaging test. Imaging tests computed tomography (CT) scans, Positron Emission Tomography (PET), or ultrasound may include.
- The genetic test. In some people with medullary thyroid cancer endocrine cancer watch with other genetic changes that can can be found. Your family history, to search for genes that increase your risk of cancer, your doctor warn you about the premise of a genetic test.
What are the types of thyroid cancer?
The type of thyroid cancer determines treatment and the course of the disease. Types of thyroid cancer include the following:- Papillary thyroid cancer. Which is the most common type of thyroid cancer papillary thyroid cancer originates from the follicular cells produces and stores thyroid hormones. Papillary thyroid cancer can occur at any age but most commonly affects people between the ages of 30 and 50.
- Follicular thyroid cancer. Start in the follicular cells of the thyroid follicular thyroid cancer. It usually affects people over the age of 50. Hurthle cell cancer is rare and potentially more aggressive follicular thyroid cancer follicular thyroid cancer is a type of.
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer. The thyroid C cells that produces calcitonin a hormone called, starts in the cells of the thyroid. Rising TSH levels in the blood may indicate the very early stages of thyroid cancer. Certain genetic syndromes increase the risk of medullary thyroid cancer, although this genetic link are not common.
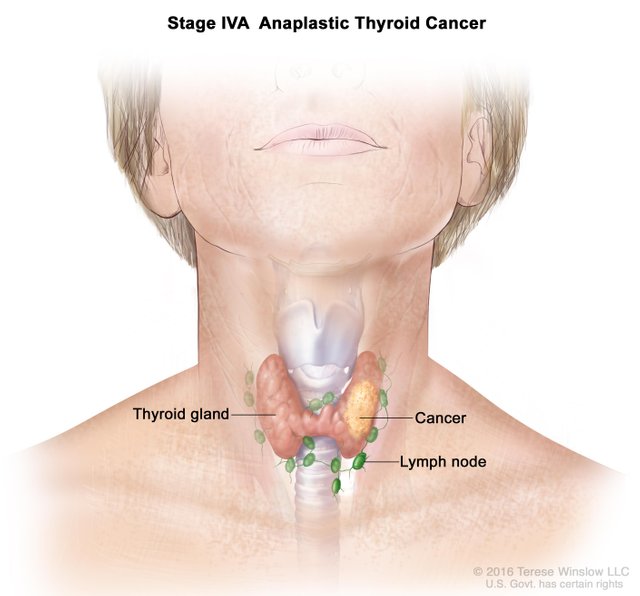
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer. Anaplastic thyroid cancer, which is rare and very difficult to treat fast-growing cancer. Anaplastic thyroid cancer typically occurs in adults over the age of 60.
- Thyroid lymphoma. Thyroid lymphoma begins in cells of the immune system and rapidly growing in the thyroid gland is a rare type of thyroid cancer. Thyroid lymphoma typically is seen in older adults.
What are the treatments for thyroid cancer?
Your thyroid cancer treatment options the stage of the cancer, your overall health depends on your preferences.Most cases of thyroid cancer can be cured with treatment.
Surgery
Parathyroid glands
Most people with thyroid cancer of the thyroid gland is removed all or most of the surgery. Following surgery to treat thyroid cancer includes:
- The removal of all or most of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy). In most cases, doctors recommends the complete removal of the thyroid gland to treat thyroid gland. Your doctor makes an incision at the base of your neck for thyroid access.
- Removal of lymph nodes in the neck. While your doctor your thyroid in your neck enlarged lymph nodes take out cancer cells in terms of them can be tested.
- Surgery to remove part of the thyroid (thyroid lobectomy). In some cases where thyroid cancer is very small, your surgeon only one side of the thyroid gland (lobes) may be recommended.
Thyroid hormone treatment
After thyroidectomy the thyroid hormone levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Synthroid, and others) you will use all your life.
There are two benefits of these drugs: Thyroid hormone that under normal conditions it will produce a lack of substitutes and the pituitary thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and suppresses the production of. It is probable that high TSH levels stimulate any remaining cancer cells to grow.
Until you find the correct dose for your doctor to check your thyroid hormone level, you will probably have a blood test in a few months. Blood tests may continue on an annual basis.
Radioactive Iodine
Radioactive iodine, the radioactive form of iodine high doses of uses.
Radioactive iodine treatment, which were not removed during the surgery as well as remaining healthy thyroid tissue of thyroid cancer after thyroidectomy to destroy microscopic fields are often used. Radioactive iodine treatment after treatment, recurrent or has spread to other parts of the body also that can be used in the treatment of thyroid cancer.
Radioactive iodine treatment, presumably, is given as a capsule or a liquid. Hashimoto's disease and thyroid cancer radioactive iodine taken up primarily by cells and thus the risk of harm to the other cells in your body is low.
Side effects may include the following:
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Dry eye
- Change in smell or taste sensation
- Fatigue
External Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, X-rays and high energy electrons such as X-rays using a machine that directs you to the right spot in your body may be given from outside(external radiation therapy). Typically this treatment is applied five days a week for five weeks for approximately a few minutes at a time. During the treatment, you shall lie down on a table of a machine moving around.
External beam radiation therapy, or surgery if you are unable to, and if it continues to grow after radioactive iodine treatment for cancer may be an option. An increased risk of recurrence if your cancer has radiation therapy after surgery may be recommended.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, which uses chemicals to kill cancer cells medication. Chemotherapy typically from a vein, it is provided in the form of infusion. Chemicals spread throughout your body, including cancer cells, they will kill fast growing cells.
Chemotherapy is not commonly used in the treatment of thyroid cancer, but some people do not respond to other treatments that can be useful. Chemotherapy can be combined with radiation therapy in anaplastic thyroid cancer.
Injecting alcohol into the cancer
Alcohol ablation, an ultrasound imaging to ensure exact injection using a method like that are not in the right place, involves injecting small thyroid cancers with alcohol into. This treatment easily arise in areas that are inaccessible during the surgery is beneficial in the treatment of cancers that. Limited to a small region in your neck your doctor if you have anaplastic thyroid cancer, this treatment may suggest.
Targeted drug therapy
Targeted drug therapy uses specific remedies cancer cells attacking your weaknesses.
Targeted drugs used to treat thyroid cancer include the following:
- Cabozantinib (Cosmetiq)
- Sorafenib Which Was Originally (Nexavar)
- Vandetanib (Caprelsa)
Supportive (palliative) care
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on pain and to alleviate the symptoms of other serious diseases. Palliative care specialists, care that complement your ongoing support separate layer in order to provide you, your family, and work in conjunction with other physicians. Palliative care, surgery, chemotherapy or other aggressive treatments such as radiation therapy can be used as continue.
When used in conjunction with all other appropriate treatments, palliative care, people with cancer themselves, they can feel better and live longer.
In palliative care doctors, nurses, and other health professionals, provided by a team of specially trained. Palliative care teams aim to increase the quality of life of people with cancer and their families. This type of care that you may receive a healing treatment, or along with other therapies, is presented.
source: neolife.com
Posted from my blog with SteemPress : https://www.orak11.com/index.php/2018/09/04/what-is-thyroid-cancer/