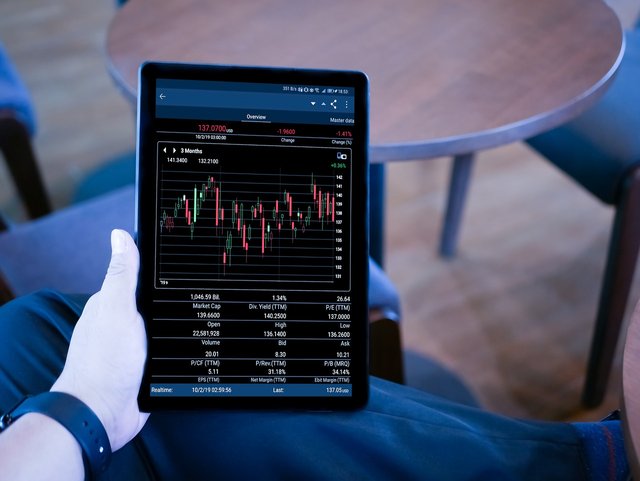
A Forex trading platform consists of various components and features that enable traders to execute currency exchange transactions. Here are the key elements typically found in a Forex trading platform:
User Interface (UI): The user interface is the graphical part of the platform where traders interact. It includes charts, price quotes, trade execution buttons, and account information.
Currency Pairs: A Forex trading platform allows traders to select and trade various currency pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar), GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen), and many others.
Real-Time Price Quotes: The platform provides real-time or delayed price quotes for currency pairs. Traders use these quotes to analyze market conditions and make trading decisions.
Charts: Charting tools are essential for technical analysis. Forex platforms offer various chart types (candlestick, line, bar) and timeframes (e.g., 1-minute, 1-hour) for traders to analyze price movements.
Technical Indicators: Platforms often include a wide range of technical indicators (e.g., moving averages, RSI, MACD) that traders can add to their charts to aid in decision-making.
Order Types: Traders can place different types of orders, including market orders (buy or sell at the current market price), limit orders (buy or sell at a specific price), and stop orders (buy or sell once the price reaches a certain level).
Risk Management Tools: Forex platforms typically offer risk management tools like stop-loss and take-profit orders, allowing traders to set predefined exit points to limit losses or secure profits.
Account Information: Traders can access their account balance, margin levels, equity, and trade history through the platform.
News and Analysis: Some platforms provide access to real-time news feeds and fundamental analysis tools to help traders stay informed about economic events and news that may impact currency markets.
Alerts and Notifications: Traders can set up alerts and notifications based on specific price conditions or news events, keeping them informed even when they are not actively using the platform.
Mobile and Desktop Versions: Many Forex platforms offer both desktop and mobile versions, allowing traders to access the market from their computers, smartphones, or tablets.
Customer Support: Access to customer support, including live chat, email, or phone assistance, is essential for resolving platform-related issues or inquiries.
Security Measures: Platforms prioritize security, employing encryption and authentication methods to protect user data and transactions.
Education and Training: Some platforms offer educational resources, tutorials, and trading guides to help traders learn and improve their trading skills.
Demo Accounts: To practice trading without risking real money, most platforms provide demo accounts where traders can execute simulated trades using virtual funds.
Broker Integration: Forex platforms are often linked to specific brokers, allowing traders to open and manage their brokerage accounts directly from the platform.
It's important for traders to choose a Forex trading platform that aligns with their trading style, preferences, and objectives. Additionally, conducting thorough research on the platform's reliability, reputation, and security is essential before opening a live trading account.