Later this month, trading will begin on the Leverj platform. This will lead to fees being sent to the Staking Contract that creates and distributes FEE tokens to LEV holders who stake in the same time period. The contract process is complex but the user experience should be seamless. It is important that Leverj users get to understand LEV staking properly now, so you can decide if staking is for you.
Staking of LEV is one of the most innovative features of Leverj as a project. Staking periods occur perpetually, one after the other, where users can send their LEV tokens to the Staking Smart Contract and receive FEE tokens based on platform volume.
Here is a visualisation of how the Staking process works in infographic:
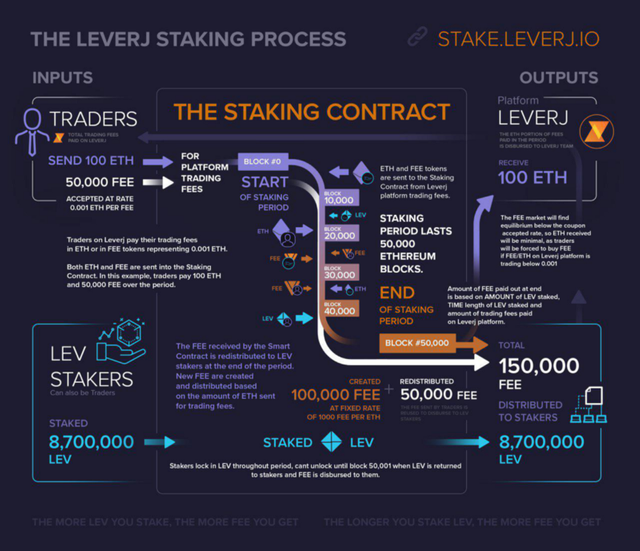
Infographic to Provide a Visualization of a LEV Staking Period
To Stake or Not to Stake
When you stake your LEV tokens, you are sending your LEV to a Staking Contract address built by the Leverj team and audited numerous times, both internally and externally. The contract is coded to give you back your LEV tokens at the end of the staking period no matter what.
There is an expected flow in FEE tokens from the LEV you stake for η blocks. However, there is a solvency risk ρ that the Staking Contract is insecure and could be hacked to steal the LEV and ETH inside it. If you believe ρ > 0 then it is safer for you to keep your LEV in a hardware wallet or paper wallet with the private key safe in your possession.
If you believe that the reward outweighs the risk that your LEV disappears in the staking process, then staking might make sense for you.
You also have the market risk that LEV price drops during time η while you are staking and unable to sell. Traders are at the mercy of liquidity and if your tokens are locked up then you are facing significant market risk in volatile episodes. If you value being nimble in the market then you won’t want to lock your tokens up too long by staking. However, by not staking you are foregoing the FEE disbursement that you would have received — which represents how how much you value that freedom to move LEV.
In the end it is about personal preference and risk tolerance. Some people will prefer to just HODL offline to avoid the hassle, some people will prefer to stake perpetually, some people will prefer to stake sometimes, trade other times. As the trading platform gets more successful, the incentive to stake will rise, as people want a piece of the pie in the form of FEE tokens.
Token Economics
All trading fees on Leverj, in FEE token or ETH, go through the Staking Contract. It is a fully self-regulating system that only produces new FEE when the market value of FEE is so high that people prefer to pay fees in ETH. The Staking Contract:
- Only creates new FEE when ETH is sent to it
- Recycles any FEE received to redistribute to stakers
ETH is only logically going to be sent to the Staking Contract if FEE tokens are for sale at coupon value or more. Otherwise, users would rationally buy FEE for less and get a discount on trading activity instead of paying in ETH.
How Many FEE tokens Will You Get When Staking?
This is one of the most common questions regarding the LEV staking system. The simple answer is that it varies from period to period so there is no way to make it fixed or more certain. The amount of FEE you receive when staking your LEV over a certain period depends on many variables: the amount of LEV you are staking, amount of total LEV being staked, how long you are staking, how long the other LEV stakers are staking, and how many platform fees are processed. This boils down to three main factors in how much FEE you receive:
- Amount of fees paid on Leverj platform over the staking period. (Total between ETH and FEE tokens at 0.001 FEE/ETH). All markets on Leverj will charge fees, except for the FEE/ETH orderbook. Therefore, the more volume there is on the platform the more FEE and ETH will be going through the staking contract over the period.
Ceteris paribus: the more fees paid by traders on Leverj exchange, the more FEE tokens will be disbursed to you and other LEV stakers. - Number of LEV tokens you and other people are staking over the period. If you are the only person staking in the whole period and you stake 1 single LEV token, then you will get 100% of the FEE generated. As the number of other people who are staking LEV is increasing in addition to yours, the less FEE you will get. So if you stake 250,000 LEV and others take 750,000 LEV, you will get more fees than if others are staking 9,000,000 LEV, since your LEV is now a smaller proportion. Ceteris paribus: the more LEV you stake, the more FEE tokens you will receive.
- The length of time your LEV tokens are staked in the period. LEV holders who keep their tokens locked up in staking contract longer are rewarded more than those who stake for less time. Your cut of the FEE disbursement at end of the staking period depends on your LEV-blocks (i.e., the number of LEV you are staking multiplied by how many blocks you are staking). This means if Bob and Alice both stake 100,000 LEV, but Bob stakes at the beginning of the period and Alice stakes at the end, then Bob will get more FEE than Alice despite staking the same number of LEV.
Ceteris paribus: the more time (in Ethereum blocks) that you are staking, the more FEE tokens you will receive.
Those are the main three considerations. If you want to maximise the FEE you receive, just stake as much LEV as you have for as long as the staking contract is alive. The more volume the Leverj platform does, charging more fees, the more FEE tokens will be created and redistributed to LEV stakers.
FEE Tokens as Coupons
Leverj is an ERC20 spot and derivatives exchange that charges all fees in ETH. Each FEE token gets you 0.0010 ETH worth of trading fees on Leverj, and a free market for FEE/ETH is available to buy and sell FEE (we will be charging 0% for this pair). For example, if you make an trade which costs you 0.033 ETH, then you can pay this in 33 FEE instead of in ETH. This means if you can buy FEE tokens from the FEE/ETH orderbook for, say, 0.0008 ETH, then you pay 0.0264 ETH for the 33 FEE that will cover your trading cost. That saves you 0.0066 ETH by buying these “coupons” from LEV stakers who are not interested to use them to trade on the platform right away.
In the early stages, FEE may be trading at erratic prices, as the platform initially won’t require users to buy FEE. If there is no FEE for sale at below 0.001 ETH then a user will just pay ETH for their fees on Leverj ERC20 spot exchange (all fees are charged in ETH).
FEE Price in ERC20 Token Market
As the FEE market matures, it should stabilise at a discount, anywhere from between 60–95% of the coupon face value of 0.0010 ETH.
A market will be made between:
- Supply: LEV stakers who just want to sell their FEE disbursed every week to get some ETH (e.g., early TGE participant just staking LEV to get FEE)
- Demand: Traders on Leverj platform who are going to pay trading fees anyway and can buy FEE for <0.0010 ETH. (e.g., 0.0008 to cover 0.0010 ETH of costs)
As an ERC20 token, FEE can be traded anywhere that chooses to list it as well, however our platform will be integrated into our own FEE market to make market operations easier. There will be slowly introduced a mechanism that forces users to buy FEE from the Leverj FEE/ETH orderbook if the price is cheaper than paying in ETH. This will provide an adequate flow of demand for FEE in case stakers are aggressively selling.
There will be a constant flow of FEE that traders on Leverj buy, which is redistributed to LEV stakers, and a market for FEE will ensure that minimal, if any, ETH will end up being sent in the long-run as all fees will be paid in FEE tokens.
Conclusion
Leverj is doing a lot of cool things:
- plasma DEX flavour to do secure highspeed trustless offchain trading
- Trustless derivatives on Ethereum
- LevPredict prediction market tokens
And don’t forget:
- A cool, functioning bi-level token model that just works!
And if you haven’t already watched the Staking Contract Webinar, check it out here.
Want to learn more?
- Check out the website
- Read our white paper
- Study our protocol
- Follow us on Twitter
- Join our Telegram group