
In order to achieve success, a strong infrastructure is needed. Often we hear terms or expressions like that in everyday life. Then, what about running a business? Is infrastructure also needed to achieve business success? What is the role of infrastructure in running the business world? What does infrastructure have to do with the business we run?
Future Projects
As the name implies, the "Entire Earth" Foundation intends to focus on all infrastructure & environmental related projects around the world. As a starting point, we are focusing on the topic of water, but the potential uses of the platform go beyond water infrastructure.
Building energy efficient buildings is another potential application area for environmental databases. Many startups in this area are pursuing innovative data-driven solutions to improve energy efficiency. However, many of these companies work with insufficient data. The data varies from company to company, so it is not possible to carry out a holistic analysis and produce optimal results.
The WEA database can bring these areas together by providing a place where environmental data related to a large number of buildings can be collected, curated and shared by companies working in this field as well as building owners. The WEC creates an incentive for companies to exchange and share this data, which is usually kept secret, benefiting all companies.
Many organizations working to upgrade different segments of their infrastructure face similar challenges, limited by the availability or lack of quality data sets ready for analysis. The Foundation plans to assist these organizations as ecosystem partners by providing shared access to databases created by the WEF community.
Provision of Ecosystem Tools
To promote the use and adoption of the WEA platform, WEF will provide a set of tools for those who wish to engage with our platform after the network launch.
The general public will be able to connect and access environmental databases and contribute data. Participation with the platform and data provision will be encouraged by exploring gamification mechanisms such as using Quest to engage users in tasks. Users can then manage and make use of the utility tokens they earn in exchange for various tasks.
Infrastructure-related service providers will have access to environmental databases. This data will enable service providers to increase the efficiency of development projects by having access to up-to-date information managed by the community. They can also take advantage of products created by third party developers.
Third party developers will also have access to the environment database. They will be encouraged to explore new data applications for projects that benefit infrastructure and the environment. The Foundation aims to work with partners to ensure all projects are in line with the foundation's vision.
An important part of implementing this approach is a method for measuring the value of the information provided. For example, if the general public provides information leading to the elimination of a water pipe leak, it is likely to succeed in helping to save water that would otherwise be lost. In other words, making water now accessible can be considered the equivalent of producing water. Therefore, the value of information stems from its ability to conserve and create resources, such as water.
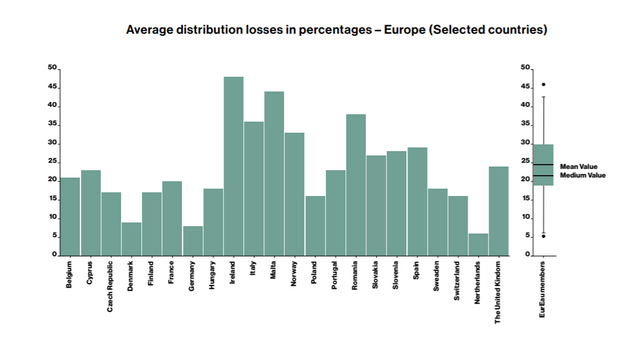
Representation in this way is a powerful method for conserving resources, maintaining infrastructure and realizing savings. For example, water that does not reach consumers from water supply stations due to reasons such as leakage in distribution pipes is usually referred to as “non-revenue water”. The amount of "non-revenue water" in Japan is equivalent to 1.6 billion USD per year - a significant amount of potential savings. Non-income water is a widespread problem in several countries, including other European and Asian countries. But we can achieve a lot more if we understand and represent saving resources as the equivalent of resource creation.
Based on this method of calculating the value of saved water resources, participants can get tokens for their data contribution efforts. Part of the process for calculating the amount to be obtained will involve using an algorithm developed by a third party developer that is designed to predict factors such as the condition of a water pipe breakdown. For example, Fracta, in partnership with WEF, has demonstrated the usefulness of environmental databases by developing sophisticated machine learning to predict water pipe failure status. By studying the detailed environmental factors captured in the database, the model allows providers to accurately anticipate which water pipes have the highest risk of failure. This enables providers to successfully take precautions to address infrastructure problems before destructive explosions occur, repair unseen leaks, and save water. Algorithms like this are expected to evolve and become more advanced in the future, achieving improved performance. Simultaneously, the size, amount of detail, and features of the database will continue to grow due to efforts to collect data from multiple sources.
Future service providers and partner organizations wishing to collaborate on projects with the Foundation, or take advantage of the Foundation's network and tools (for example, databases) can purchase WEC as a subscription fee to maintain partnerships. As the project progresses, we plan to form strategic partnerships with various organizations and create new ways to leverage the WEC token in the ecosystem. The Foundation is also actively looking for ways to use these tokens for goods and services.
Ecosystem Governance
Currently, the WEC token is an ERC20 Utility Token which is based on the Ethereum blockchain. We chose the Ethereum blockchain for its maturity as a decentralized platform that offers strong security and access to a variety of development tools. As we progress, the Foundation will actively seek out governance structures that better support our goals and take into account factors such as scalability and overall environmental impact.
Team | Leadership & Core Members & Advisors
- Takatsugu Kobayashi: CEO, Co-Founder
- Mayumi Suzuki: CFO, Co-Founder
- Hiroaki Sengoku: Fellow Engineer
- Chef Sasagawa: Senior Engineer
- Daiki Moriyama: Founding Advisor (Upcoming COO)
- Takashi Kato: Co-Founder and CEO of Fracta, Inc.
- Yumiko Nishimura: Counselor
- Jordan Breslow: Legal Counsel
Conclusion
Preserving and Creating Resources
An important part of implementing this approach is a method for measuring the value of the information provided. We hope you have enjoyed introducing our project. For more information and updates on the project, please follow our website. We also regularly provide information on social media
Complete information:
Website: https://wholeearthfoundation.org/
Whitepaper: https://wholeearthfoundation.org/WEF-whitepaper_v1.0.pdf
Telegram: https://t.me/WholeEarthFoundation
Twitter: https://twitter.com / WholeEarthFdn
Media: https://medium.com/wholeearthfoundation
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/WholeEarthFoundation/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/WholeEarthFoundation
Author: Homio
Bitcointalk: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=2865336
My ERC20 Wallet: 0x3e9D0A5f1eA321a35AAec9629827123860d7Ea09