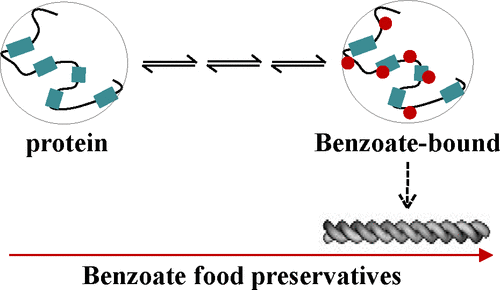
Benzoic acid and its methyl and propyl para-hydroxy derivatives are approved food preservatives and flavoring agents. Inclusive use of these additives in food, pharmaceuticals, and beauty and healthcare industries however raises concern about the quality and shelf life of the products. The safety levels of benzoates are controversial, even though studies have indicated that they may produce adverse health effects. This study employs nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), infrared (IR), fluorescence anisotropy, the molecular docking approach, and electron microscopy to examine lysozyme, myoglobin, and cytochrome c under acidic and neutral-pH conditions and finds that benzoates bind to multiple independent sites on proteins by hydrogen-bonding and π-stacking interactions, although electrostatic interactions may also appear as neutral-pH conditions are approached. The benzoate-bound proteins enter the aggregation pathway to produce amorphous and perhaps occasional fibrillar structures. The concentration of benzoates needed to induce protein aggregation is much lower than the microbicidal and inhibitory concentrations prescribed by Food and Agriculture Organization of the United state.
Authors get paid when people like you upvote their post.
If you enjoyed what you read here, create your account today and start earning FREE STEEM!
If you enjoyed what you read here, create your account today and start earning FREE STEEM!