(ESO / C. Opitom et al. https://bit.ly/3LX2zSj)
A team of British astronomers analyzed the material ejected from the Dimorph asteroid as a result of impact by the DART probe.
The researchers used the ground-based VLT telescope and they did not find traces of fuel and water vapor in the composition.
At the same time, scientists observed the evolution of the ejection and determined that the level of polarization of sunlight reflected from it fell after the impact.
The DART probe was launched into space in November 2021 and 10 months later reached the 160-meter asteroid Dimorph, which forms a binary system with the larger asteroid Didymos.
On September 26, 2022, DART collided with Dimorphos in a controlled manner, significantly changing the period of rotation of the asteroid around Didymos.
The mission confirmed the effectiveness of the kinetic ram as a method of planetary defense.
However, observational data on Dimorph before and after the impact are also important for evaluating the information about the properties of the Dimorph and its composition.
THE FIRST STUDY
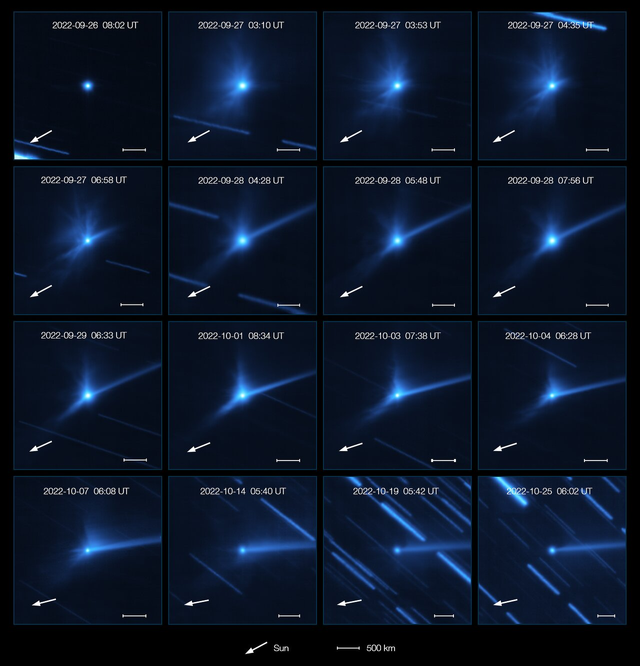
Now, astronomers led by Cyrielle Opitom (University of Edinburgh) presented the results of an analysis of data from optical observations of Dimorphos.
They used the MUSE instrument installed on one of the telescopes of the ground-based VLT complex, which started shortly before the impact and continued until October 25, 2022.
The scientists did not detect any emission in the [OI], Xe, NH2, or H2O+ lines.
This is interpreted as the absence of water vapor and fuel for the DART propulsion system in the ejection of matter from the surface of Dimorphos.
In the images, the team noticed that first a cloud of ejected material formed , which turned into a cone, and then spiral structures and a tail.
At the same time, the dust particles in the tail and spiral structures were larger than the dust particles in the initial ejection.
A SECOND VIEW
Another group of astronomers, led by Stefano Bagnulo (Armagh Observatory) analyzed optical spectropolarimetric observations of Dimorphos.
The team made the observations with the FORS2 instrument mounted on the VLT between August 23 and October 24, 2022.
The astronomers determined that before the impact, the linear polarization of solar radiation reflected from the surface of Dimorphos was at the level of 4.5%-5%.
Then, after the impact the polarization fell by 0.5%-1%, while the overall brightness of the system increased.
This may be due to the fact that the particles of the dust cloud are smaller than the particles of matter on the surface of the asteroid
Another hypothesis is that particles of matter were ejected during the collision from deeper layers of the asteroid that were not subject to weathering.
The absence of any noticeable change in the shape of the polarization spectrum after the impact suggests that the change in the level of polarization is associated with the composition of the observed material, and not its bulk structure.
Sources:
- Astronomy & Astrophysics: https://www.aanda.org/component/article?access=doi&doi=10.1051/0004-6361/202345960
- The Astrophysical Journal Letters: https://www.eso.org/public/archives/releases/sciencepapers/eso2303/eso2303a.pdf
- Interesting Engineering: https://interestingengineering.com/science/esos-vlt-dart-asteroid-impact
Wanna relax, sleep or improve your focus?
Check this rain sound video: https://bit.ly/rainsfocus
#science #space #asteroid #dimorphos #telescope #upex #nftmc
Thank you, friend!


I'm @steem.history, who is steem witness.
Thank you for witnessvoting for me.
please click it!
(Go to https://steemit.com/~witnesses and type fbslo at the bottom of the page)
The weight is reduced because of the lack of Voting Power. If you vote for me as a witness, you can get my little vote.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit