Introduction
Since the origin of blockchain technology, multiple applications have been developed, mainly digested to the management of finances, all managed by consensus mechanisms and protocols that provide functionality.
Now, it is necessary to emphasize that the consensus algorithm has been a key element within those multiple applications, as consensus algorithms directly affect the security and performance of their blockchain platforms.
Within the consensus algorithms that directly affect the security and performance of blockchain platforms, to date the most widely accepted are; Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS)and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), as they are the ones that show certain stability and operational efficiency.
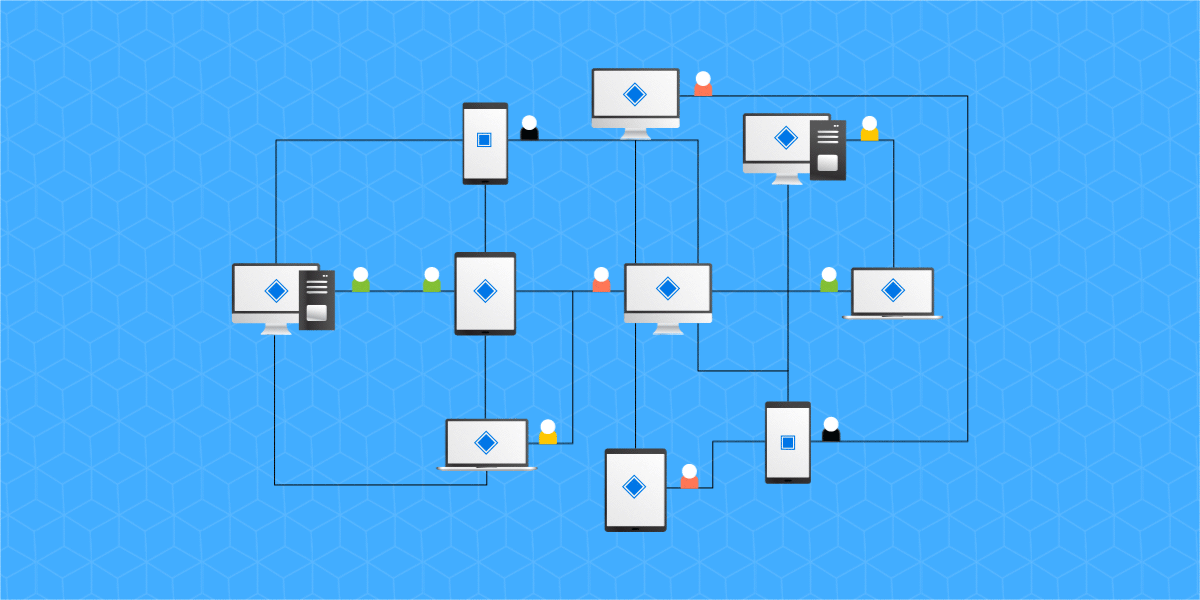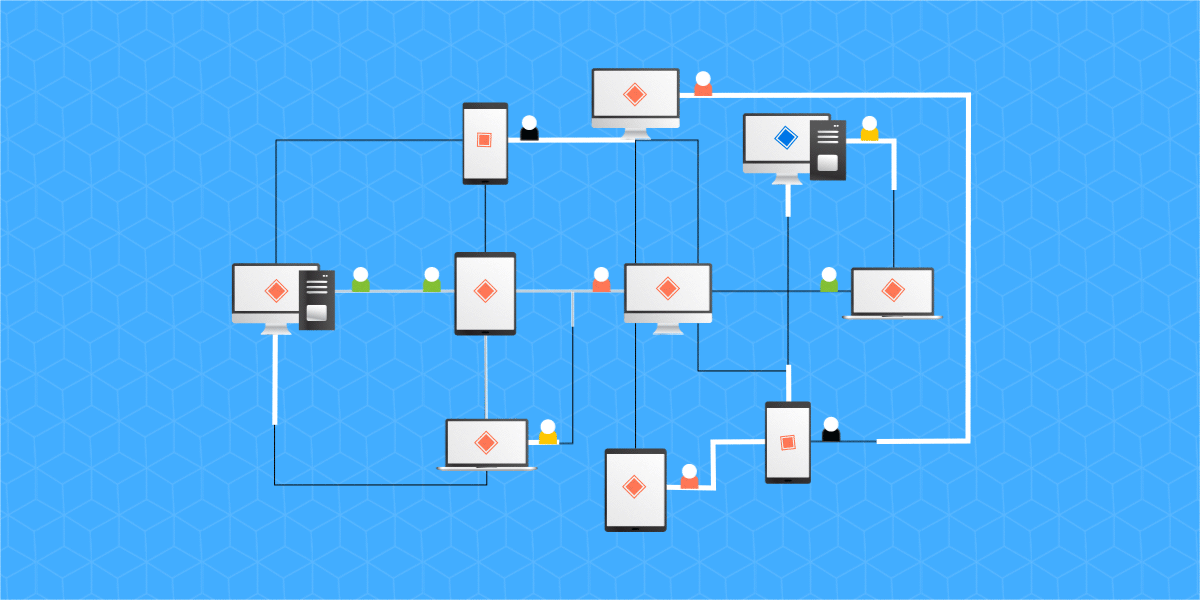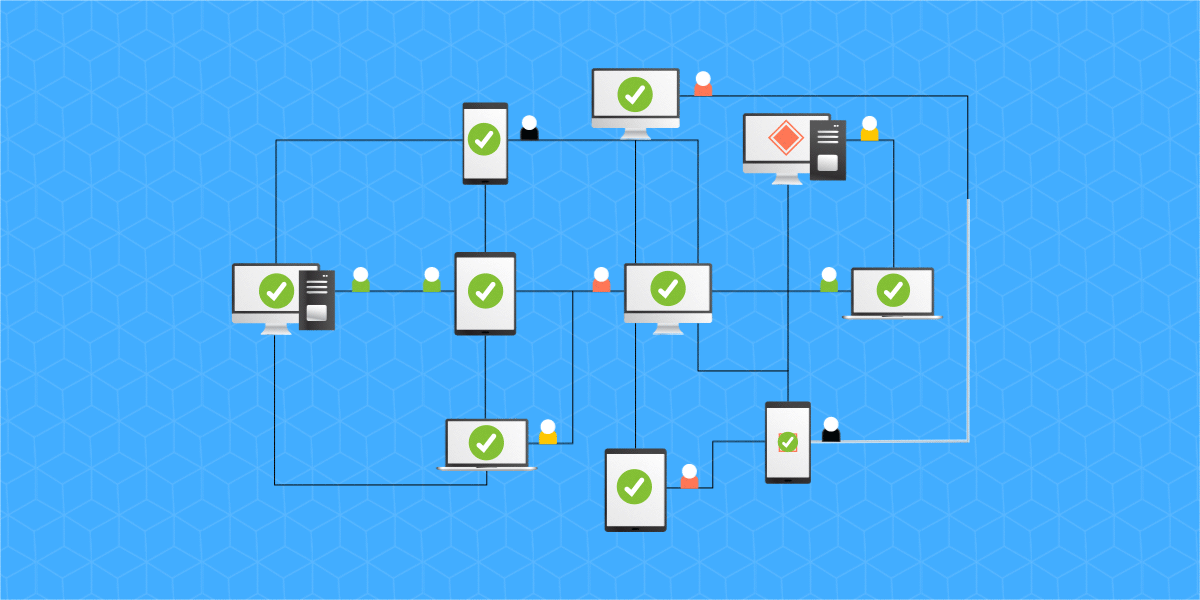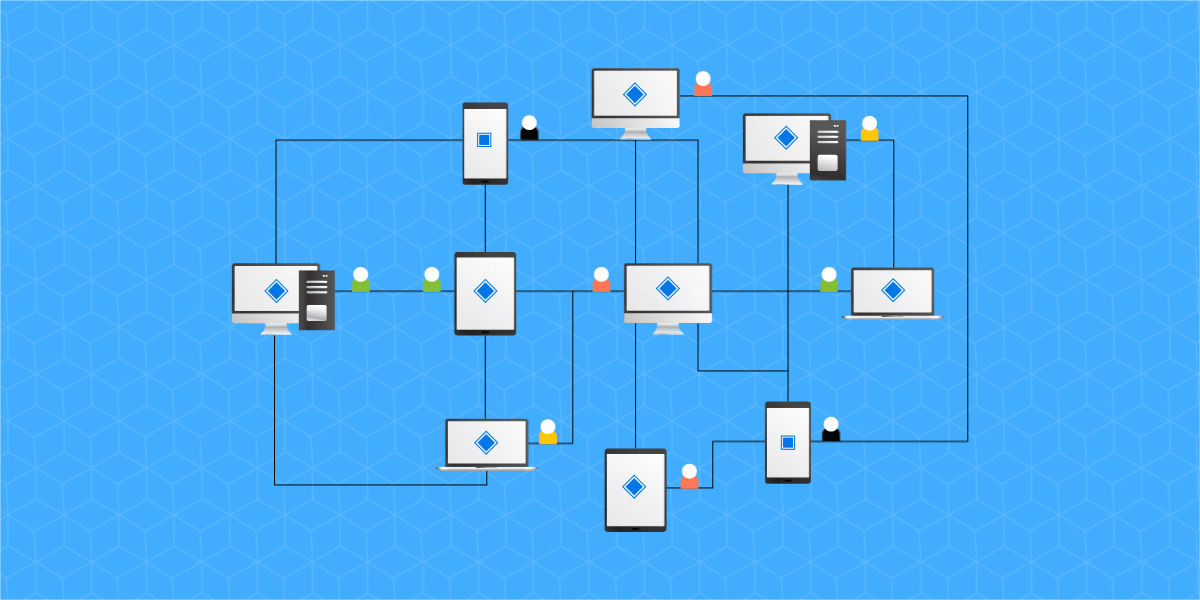
The governance of ecosystems that use the PoS concession mechanism rely heavily on computing power, as they need to spend a lot of computing resources, while DPoS introduces a PoS-based voting mechanism that reduces the cost of block generation time, this element that imprints efficiency and somehow makes the number of people entitled to participate in the operation of ecosystems using DPoS to be reduced.
It is necessary to emphasize that the consensus algorithm is the most important factor in the entire blockchain system, as its efficiency directly determines the performance of a given blockchain.
Another element to highlight, is that with the continuous development of blockchain technology, consensus algorithms are constantly adapting to emerging requirements, from the first "Proof of Work" (PoW) through the later "Proof of Stake" (PoS), and "Delegated Proof of Stake" (DPoS), to the newest consensus algorithms that have been launched to date, which have undoubtedly positively impacted the entire blockchain.
The "Proof of Stake" (PoS) concession system works as a kind of meritocratic mechanism, i.e. the operation of this consensus protocol is based on the participation of the users who validate the blocks in a given blockchain network, therefore, the greater the participation of the users, the more likely they are to be selected within the block governance and validation mechanism.
Unlike the "Proof of Stake" (PoS) concession system, the "Delegated Proof of Stake" (DPoS) consensus mechanism is less meritocratic and therefore more democratic, with the particularity that it breaks the cycle of competition in computing resources to generate blocks, and additionally introduces a voting mechanism that reduces the time cost of generating a block, and where candidates can bet a minimum amount of coins that still makes them eligible to participate as block validators.
Other differences between the POS and DPOS consensus mechanisms, the average time to generate blocks in POS is 64 s, while in DPOS it is 3 s, the governance system in POS the network is governed by randomly selected users, and in DPOS the network is governed by all users.

SOURCES CONSULTED
➊ Stefano De Angelis Assessing Security and Performances of Consensus algorithms for Permissioned Blockchains. Link

OBSERVATION:
The cover image was designed by the author: @lupafilotaxia, incorporating image background: Author: Cleversolution


@tipu curate
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 6/7) Get profit votes with @tipU :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit