Cover background image generated with AI, software used: copilot microsoft
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
[ENGLISH]
06-04-2025 - Education - Laws of Dynamics [EN]-[IT]

Image generated with AI, Microsoft Copilot
With this post I would like to provide some brief notions about the topic mentioned in the subject.
The context in which we operate is that of Physics
(code notes: MOD-90)
Laws of Dynamics
In this article we will talk about dynamics.
What is dynamics?
Dynamics is a branch of physics and studies the movement of objects together with the forces that cause and modify it. In detail we can say that dynamics analyzes the relationships between mass, force and acceleration, as described by Newton's laws of motion.
From here we have already understood that one of the most important scientists in the field of dynamics was Isaac Newton (1642-1727). He was an English scientist known for his fundamental contributions to physics.
Dynamics and Newton are strongly linked because it was the English scientist who created the foundations.
He in fact formulated:
-First law of motion (Law of inertia)
-Second law of motion
-Third law of motion
Let's briefly describe these three principles:
First law of motion
First law of motion (Law of inertia): Introduces the fundamental concept that a body remains in a state of rest or uniform rectilinear motion until an external force acts on it. This principle defines the natural state of motion of an object.
Second law of motion
The second law of motion establishes that the force (𝐹) acts proportionally to the mass (𝑚) and acceleration (𝑎), with the formula 𝐹=𝑚𝑎. This law is the heart of dynamics, as it quantitatively describes how a force causes an acceleration.
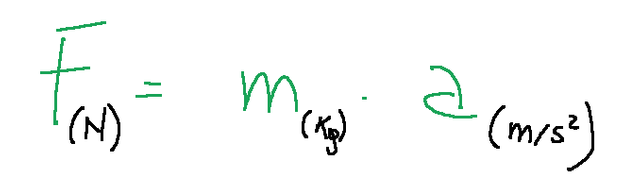
Where:
𝐹 = the force applied to the object (measured in Newtons, N).
𝑚 = the mass of the object (measured in kilograms, kg).
𝑎 = the acceleration of the object (measured in meters per second squared, m/s2).
This principle is also called:
Newton's second law
Second law of dynamics
Fundamental principle of dynamics
We can summarize the concept as follows:
This principle states that when a force 𝐹 is applied to a body of mass m, the body acquires a certain
acceleration 𝑎 (i.e. undergoes a change in velocity), according to the relationship:
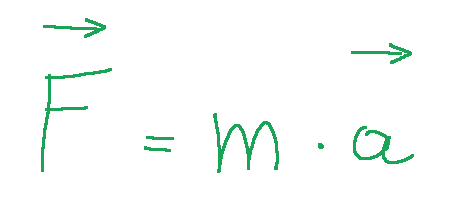
From the image above we can see that force is a vector quantity, mass is a scalar quantity, acceleration is a vector quantity.
Third law of motion
The third law of motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. This principle is essential to understand the interaction between different bodies, a key element in dynamics.
Resultant of forces
The relationship between dynamics and the resultant of forces is closely linked to Newton's second law of motion.
In fact, we can rewrite the previous relationship as follows:
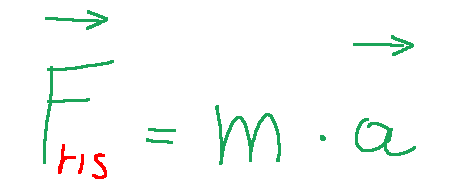
Where:
Fris = the resultant of forces, or the vector sum of all the forces applied to a body.
When multiple forces F1, F2, ... Fn act simultaneously on a material point, the effect on the motion of the point is equivalent to that of a single force R composed of the vector sum of the forces, called the resultant of forces.
The components of the resultant of forces are obtained by adding the components of the individual forces.
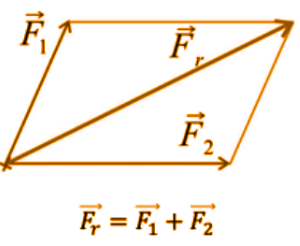
Operations with forces
With forces, all the operations that are done with vectors can be performed.
Sum of forces with different lines of action: the parallelogram rule applies.
Below is an example image
Summary of the laws of dynamics
In summary, the first law introduces the concept of inertia, the second establishes the quantitative link between force, mass and acceleration, and the third describes the mutual interaction between bodies.
Conclusions
We can say that Newton's laws of dynamics represent a fundamental pillar of classical physics, providing a clear and coherent explanation of the movement of objects and the forces that influence it.
Question
Newton lived between 1600 and 1700, he died 300 years ago. Did you know that dynamics, as formulated by Newton, is not just a theory, but a tool for interpreting the world around us?

[ITALIAN]
06-04-2025 - Education - Leggi della dinamica [EN]-[IT]

Immagine generata con IA, Microsoft Copilot
Con questo post vorrei fornire alcune brevi nozioni a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto.
Il contesto in cui operiamo è quello della Fisica
(code notes: MOD-90)
Leggi della dinamica
In questo articolo parleremo della dinamica.
Che cosa è la dinamica?
La dinamica è una branca della fisica e studia il movimento degli oggetti insieme alle forze che lo causano e lo modificano. Nel dettaglio possiamo dire che la dinamica analizza le relazioni tra massa, forza e accelerazione, come descritto dalle leggi del moto di Newton.
Già da qui abbiamo compreso che uno degli scienziati più importanti nel campo della dinamica è stato proprio Isaac Newton (1642-1727). Egli fu uno scienziato inglese noto per i suoi contributi fondamentali alla fisica.
La dinamica e Newton sono fortemente legati perché fu proprio lo scienziato inglese a crearne le basi.
Egli infatti formulò:
-Prima legge del moto (Legge di inerzia)
-Seconda legge del moto
-Terza legge del moto
Andiamo a descrivere brevemente questi tre principi:
Prima legge del moto
Prima legge del moto (Legge di inerzia): Introduce il concetto fondamentale che un corpo rimane in stato di quiete o di moto rettilineo uniforme finché non agisce su di esso una forza esterna. Questo principio definisce lo stato naturale di movimento di un oggetto.
Seconda legge del moto
La seconda legge del moto stabilisce che la forza (𝐹) agisce proporzionalmente alla massa (𝑚) e all'accelerazione (𝑎), con la formula 𝐹=𝑚𝑎. Questa legge è il cuore della dinamica, in quanto descrive quantitativamente come una forza causa un'accelerazione.
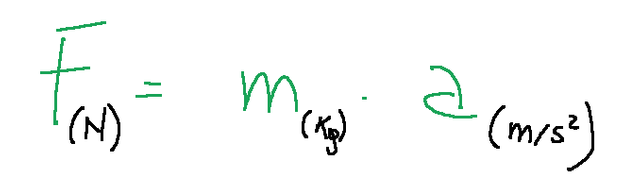
Dove:
𝐹 = la forza applicata sull'oggetto (misurata in Newton, N).
𝑚 = la massa dell'oggetto (misurata in chilogrammi, kg).
𝑎 = l'accelerazione dell'oggetto (misurata in metri al secondo quadrato, m/s2).
Questo principio è chiamato anche:
La seconda legge di Newton
Seconda legge della dinamica
Principio fondamentale della dinamica
Possiamo sintetizzare il concetto come segue:
Questo principio afferma che quando ad un corpo di massa m viene applicata una forza 𝐹, il corpo acquisisce una certa
accelerazione 𝑎 (ovvero subisce una variazione di velocità), secondo la relazione:
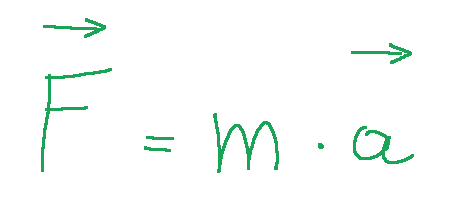
Dall'immagine qui sopra possiamo notare che la forza è una grandezza vettoriale, la massa è una grandezza scalare, l'accelerazione è una grandezza vettoriale.
Terza legge del moto
La terza legge del moto afferma che per ogni azione c'è una reazione uguale e contraria. Questo principio è essenziale per comprendere l'interazione tra corpi diversi, un elemento chiave nella dinamica.
Risultanza delle forze
La relazione tra la dinamica e la risultante delle forze è strettamente legata alla seconda legge del moto di Newton.
Possiamo infatti riscrivere la relazione di prima come segue:
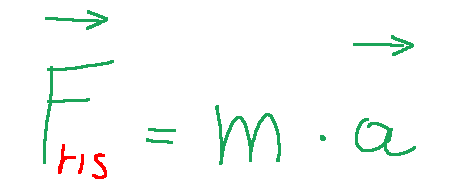
Dove:
Fris = la risultante delle forze, ovvero la somma vettoriale di tutte le forze applicate su un corpo.
Quando su un punto materiale agiscono più forze contemporaneamente F1, F2, ... Fn, l'effetto sul moto del punto equivale a quello di un'unica forza R composta dalla somma vettoriale delle forze, detta risultante delle forze.
Le componenti della risultante delle forze si ottengono sommando le componenti delle singole forze.
Operazioni con le forze
Con le forze si possono fare tutte le operazioni che si fanno con i vettori.
Somma di forze con retta di azione diversa: si applica la regola del parallelogramma.
Qui di seguito un immagine d'esempio

Sintesi sulle leggi della dinamica
In sintesi, la prima legge introduce il concetto di inerzia, la seconda stabilisce il legame quantitativo tra forza, massa e accelerazione, e la terza descrive l'interazione reciproca tra corpi.
Conclusioni
Possiamo dire che leggi della dinamica di Newton rappresentano un pilastro fondamentale della fisica classica, fornendo una spiegazione chiara e coerente del movimento degli oggetti e delle forze che lo influenzano.
Domanda
Newton visse a cavallo tra il 1600 ed il 1700, morì 300 anni fa. Lo sapevate che la dinamica, come formulata da Newton, non è solo teoria, ma uno strumento per interpretare il mondo che ci circonda?
THE END
Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This post has been upvoted by @italygame witness curation trail
If you like our work and want to support us, please consider to approve our witness
Come and visit Italy Community
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations, you have enabled UVF by @boylikegirl
Common UVF commands:
1.uvf_info
Reply any post use "!uvf_info"
Display your UVF information
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I actually remember been taught this particular topic many years ago and I must really confess that at first I didn't really understand but as time goes on, it become transparent for me to see
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Voglio dirti una cosa che NON ha nulla a che fare con il post. Mentre lavoro sento delle notizie: il VIETNAM vuole negoziare con TRUMP. il prezzo del BTC e delle criptovalute è in calo, il mio progetto è fermo, spero che altri paesi seguano l'esempio del Vietnam.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit