Hello my steemit community,

In today's edition of IMPROVING HEALTH OF STEEMIANS, I want to talk to you about Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media).
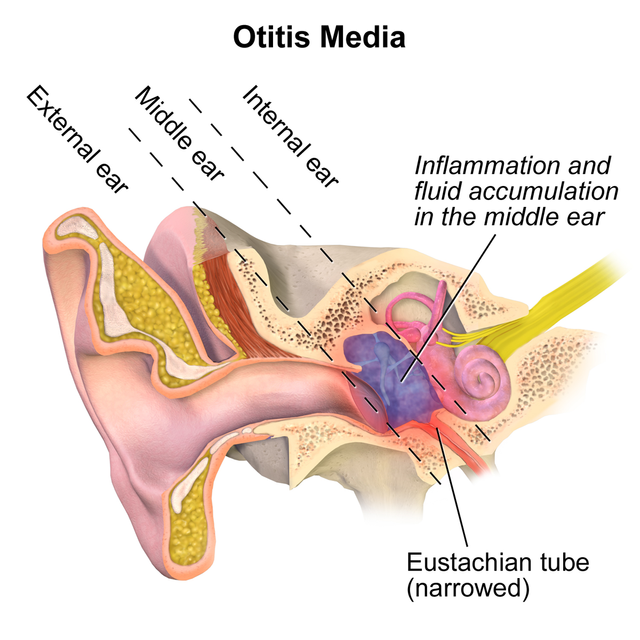
A middle ear infection, also called otitis media, is an infection of the middle ear that causes redness , swelling , and a build-up of fluid behind the eardrum. It affects 11% of people each year with half occurring in those below five years.
Anyone can develop a middle ear infection but it is most common in children. That's because a child's Eustachian tubes are narrower and shorter than an adults', and it is easier for fluid to get trapped in the middle ear.
Most otitis media occur when an infection such as a cold, leads to a build-up of mucus in the middle ear and causes the Eustachian tube to become swollen or blocked. This mean mucus can't drain away properly, making it easier for an infection to spread into the middle ear. Bacteria will often grow in the fluid, causing pain and infection. It can also be caused by the insertion of foreign bodies into the ear, including the ear picks.
The risk group for developing disease include individuals with family history of frequent ear inflammation, people living with smokers, people with poor immune systems or chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and people with abnormalities of the palate.
There are three types of otitis media :
Acute otitis media- lasts for 3 weeks in which the middle ear shows the signs and symptoms of acute inflammation
Otitis media with effusion- fluid remains trapped in the ear even after the infection is gone
Chronic otitis media- occurs if acute inflammation is not treated sufficiently and timely, if there is a pathological process in the nose, and if the mucous membrane resistance is reduced, as well as the immune system of the entire organism
SYMPTOMS
There are a variety of symptoms associated with middle ear infections. The most common are:
pain in one or both ears (Earache)
muffled hearing
a high temperature (fever)
trouble sleeping
dizziness, balance problems
nausea and / or vomiting
ear drainage
headache
DIAGNOSIS
Pneumatic otoscopy is the standard of care in the diagnosis of acute and chronic otitis media. Using an otoscope, a doctor examine the ear to look for signs of an infection.
Some other tests can be conducted, such as :
Tympanometry- to determine whether the middle ear is working properly
Audiometry- to determine if there is any hearing loss as a result of the disease
TREATMENT
The goals for treating ear infections include curing the infection, relieving pain and other symptoms, and preventing future ear infections. If a bacterial infection is present, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
Most people with acute otitis media get better without treatment.
If a person has severe or persistent pain and fever, and the eardrum is bulging, surgical procedures may be performed such as:
Tympanocentesis
Myringotomy
Myringotomy with insertion of a ventilating tube
REFERENCE
Probst R., Basic Otorhinolaryngology, Thieme, 2006.
Harmes KM, Blackwood RA, Burrows HL, Cooke JM, Harrison RV, Passamani PP.- Otitis media: diagnosis and treatment. ; Am Fam Physician. 2013 Oct 1
Factual claims which are not sourced are from my own personal experience and med school.


Interesting!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit