
The Average True Range (ATR) is a popular technical analysis indicator used to measure volatility. Developed by J. Welles Wilder, a US-based technical analyst who also developed the Relative Strength Index (RSI), the role of the ATR indicator is to simply show when volatility is high and when it is low. In this blog post, we look at the structure of this indicator and the how to profit from using it.
Structure of ATR indicator
In order to start using the ATR, you first have to calculate it. As a first step, you should identify the True Range of the period on that particular chart, which simply represents the daily high minus its low. Once the True Range is defined, you calculate the average value for the period on the chart by using an Exponential Moving Average on the values.
In general, the ATR is calculated from the 14-day moving average of a series of true range indicators. The longer the moving average period is used, the lesser number of trading signals is generated.
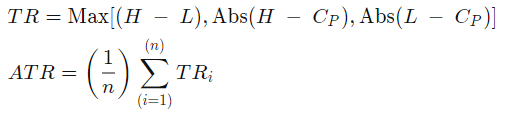
In the formula above “TRi” represents a particular true range while “n” is the time period employed. Nowadays, almost all tools offer automatically calculated ATR values, so your job is to add the indicator to the chart.
Signals of the ATR
As outlined above, the basic function of the ATR is to measure volatility of the particular financial instrument. In the photo below, we see a BTC/USD chart where the ATR suddenly bursts higher. You will see that this sudden increase in volatility overlaps with Bitcoin moving higher on the 4h chart.
Thank you for the guide https://9blz.com/rsi-indicator-explained/
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit